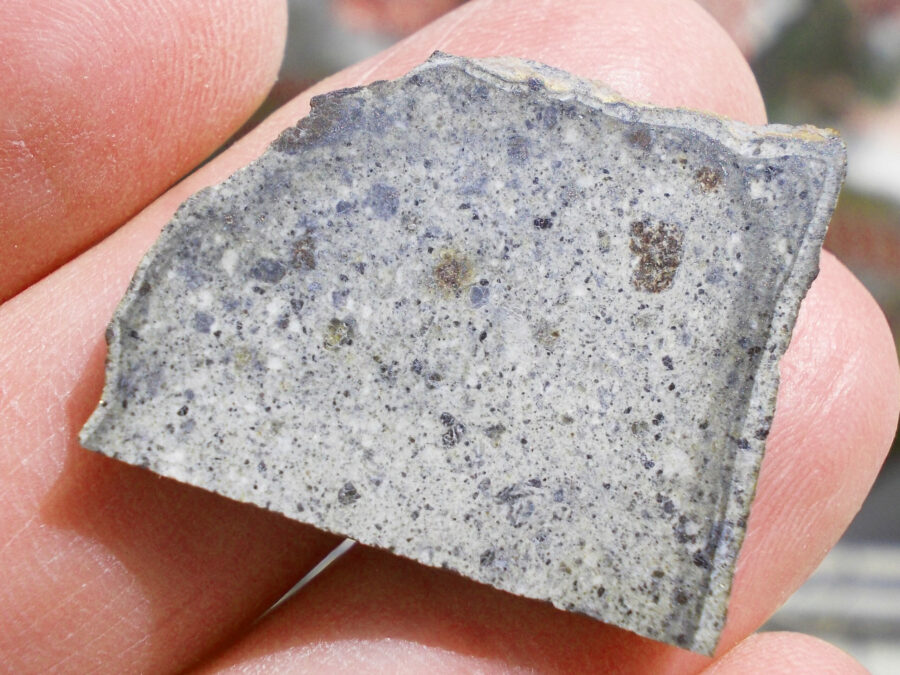
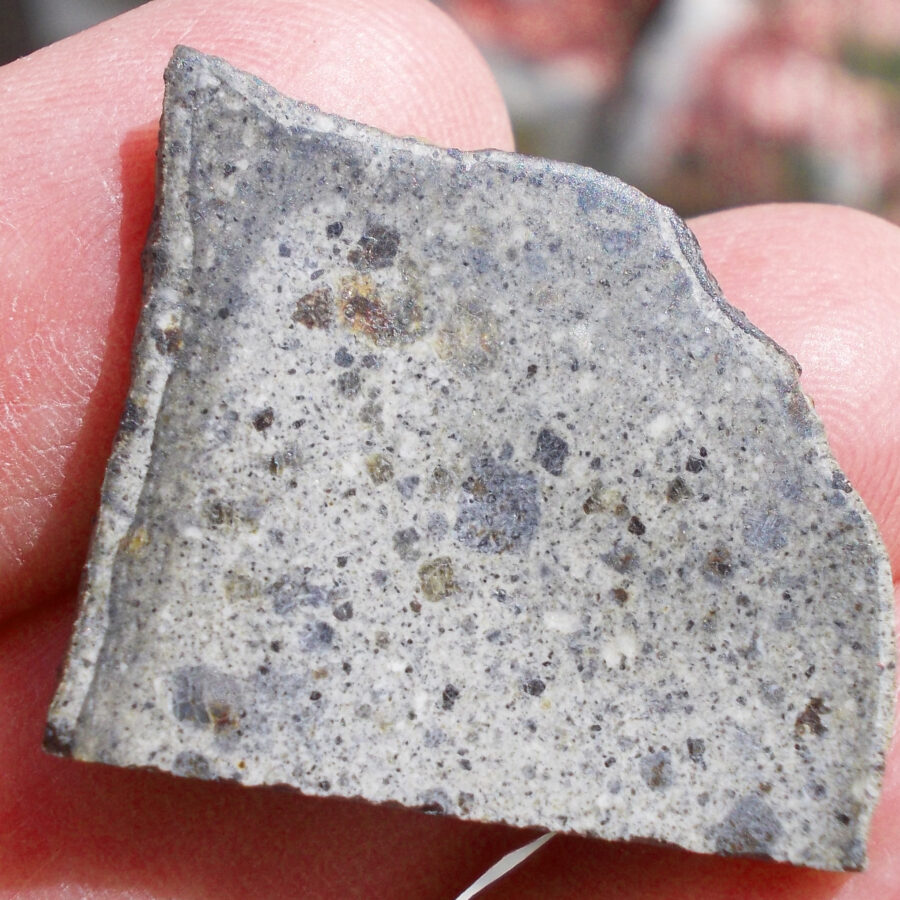
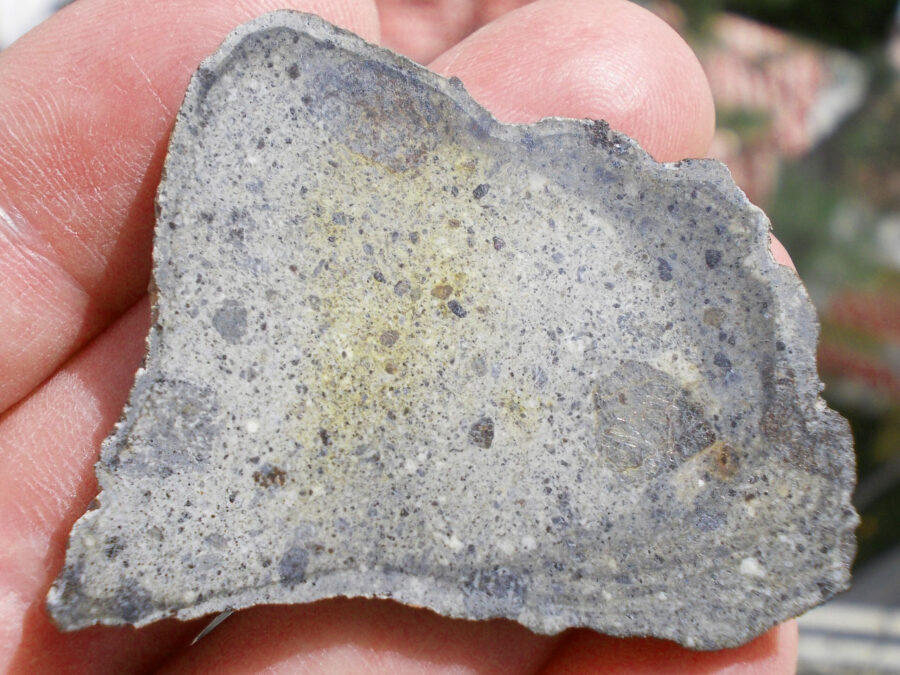
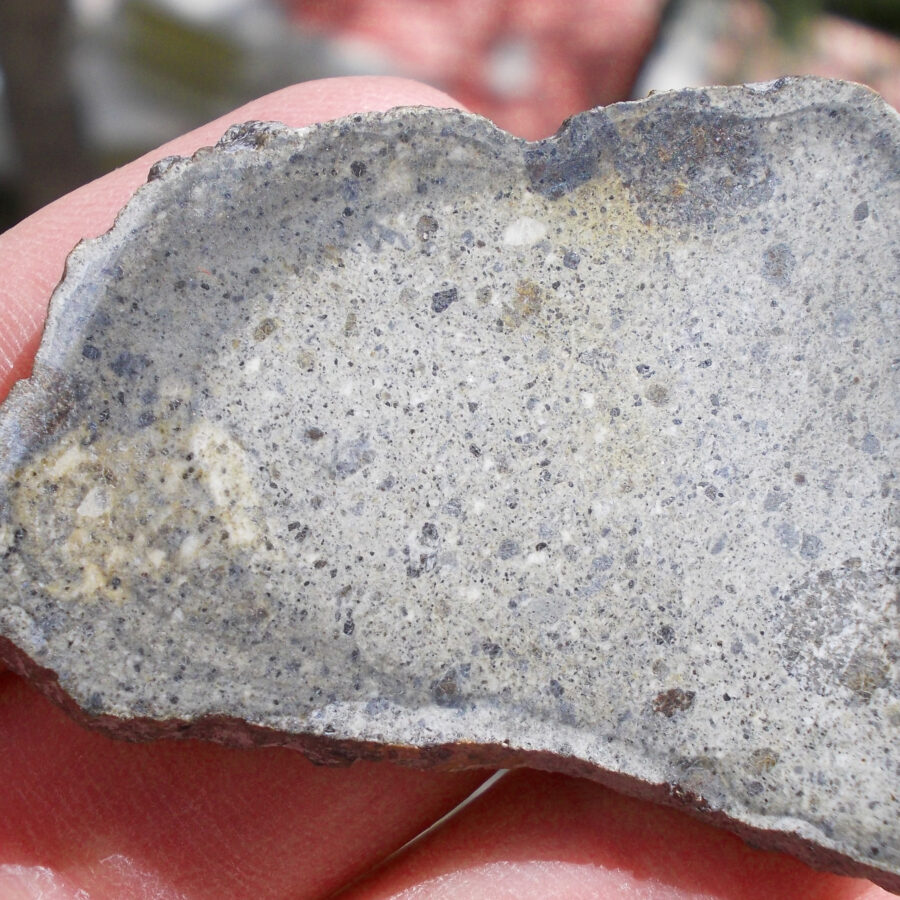
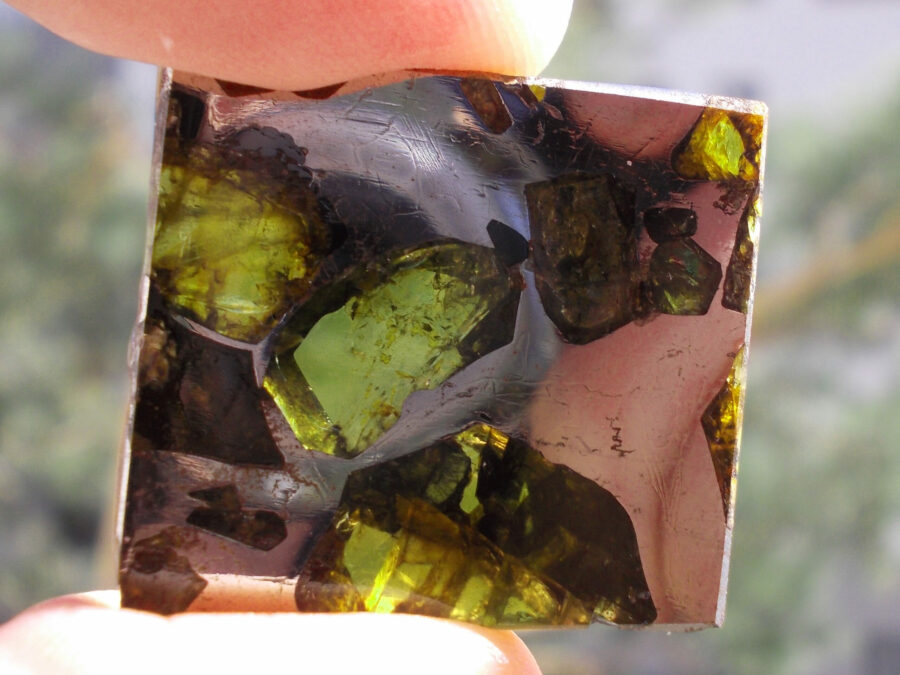
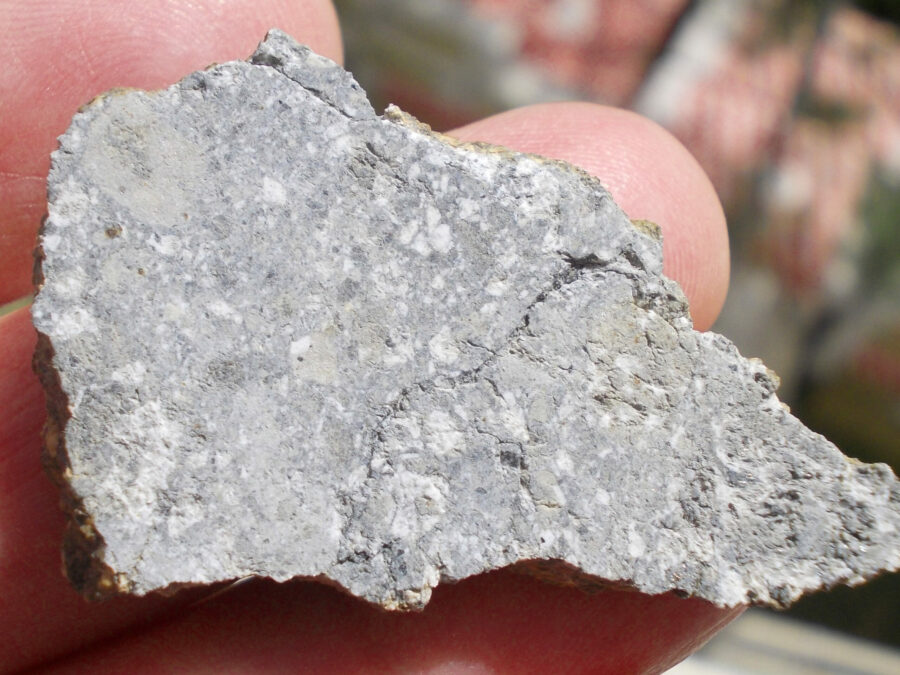
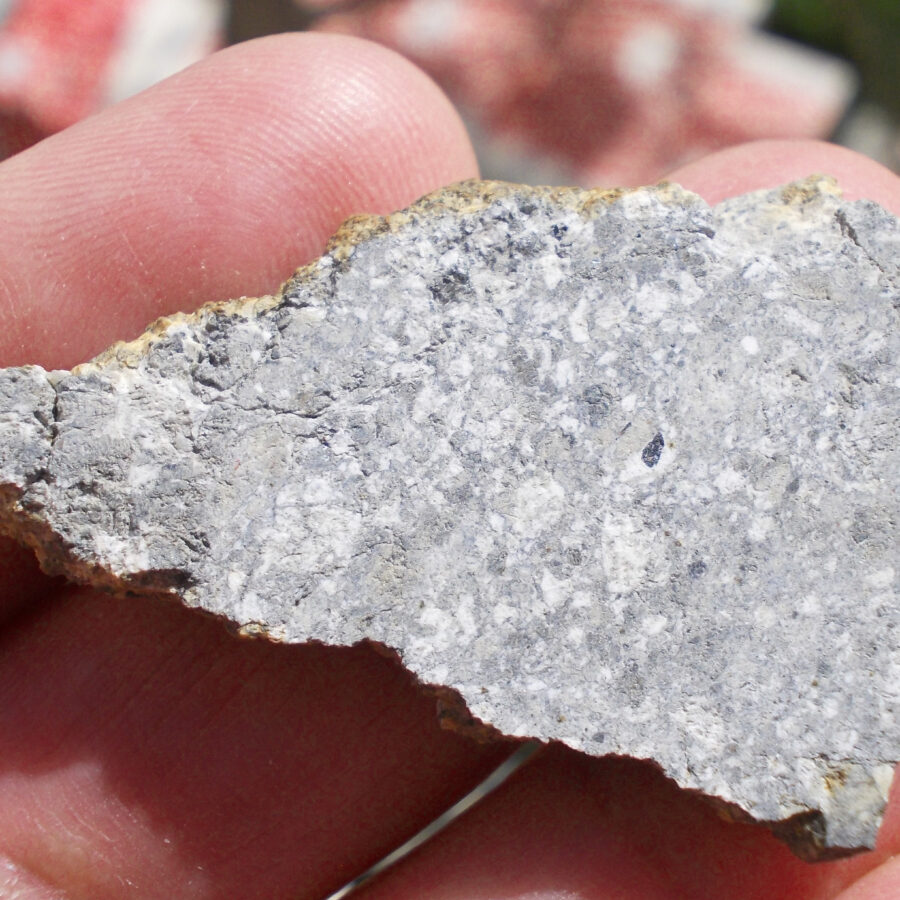
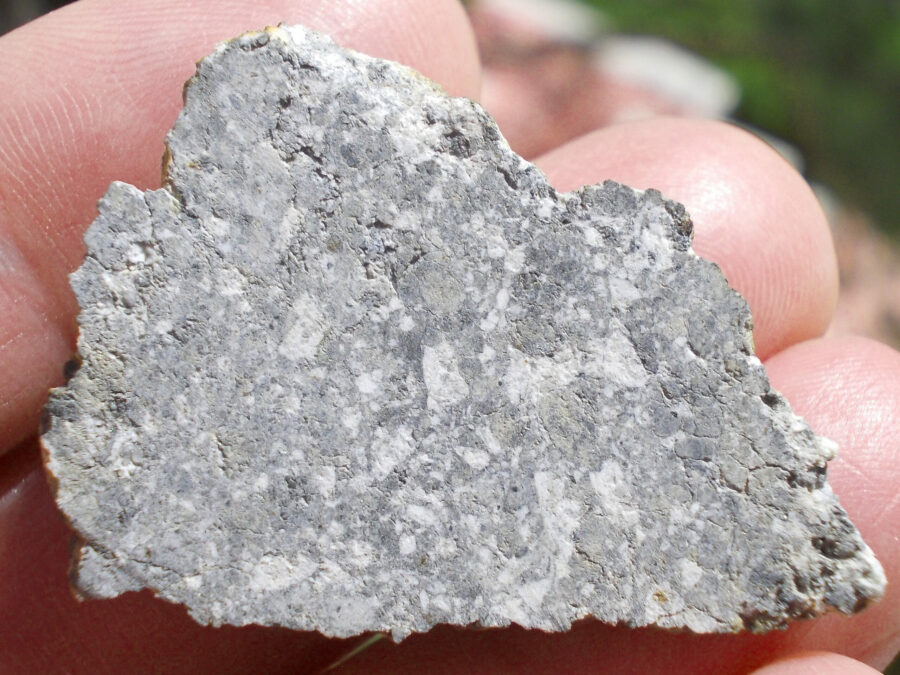
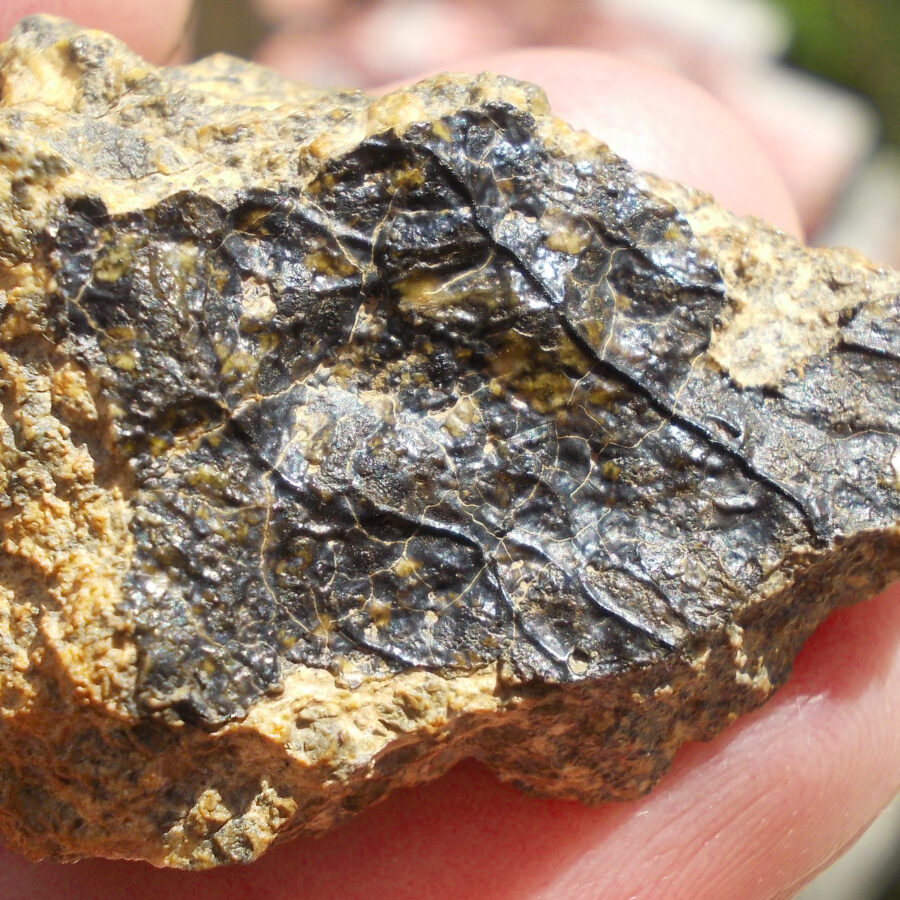
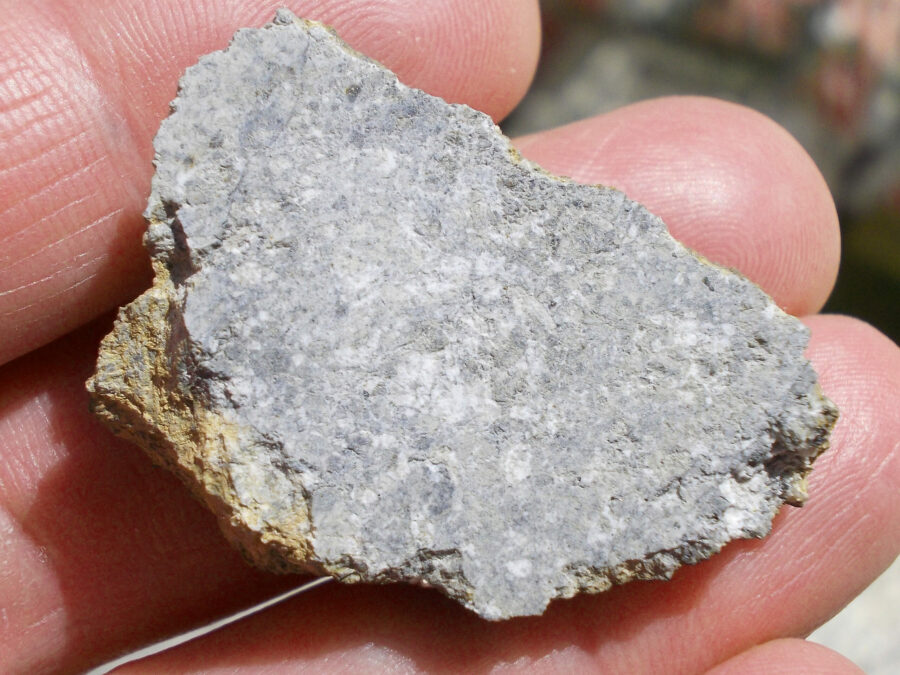
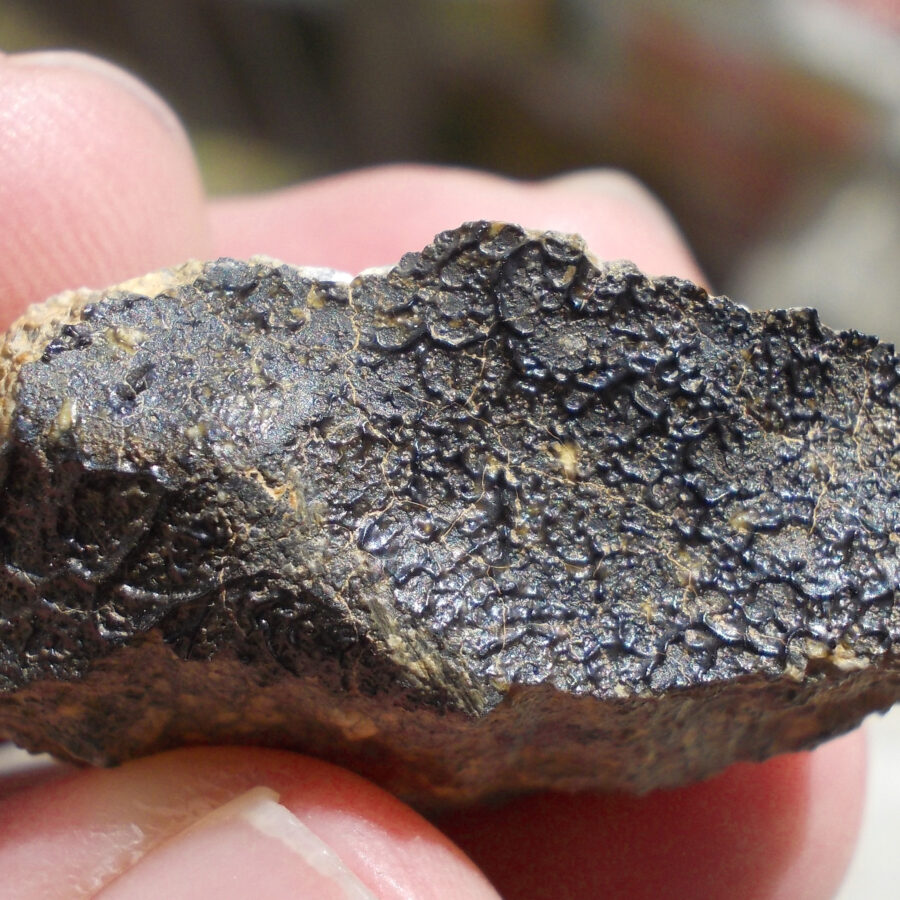
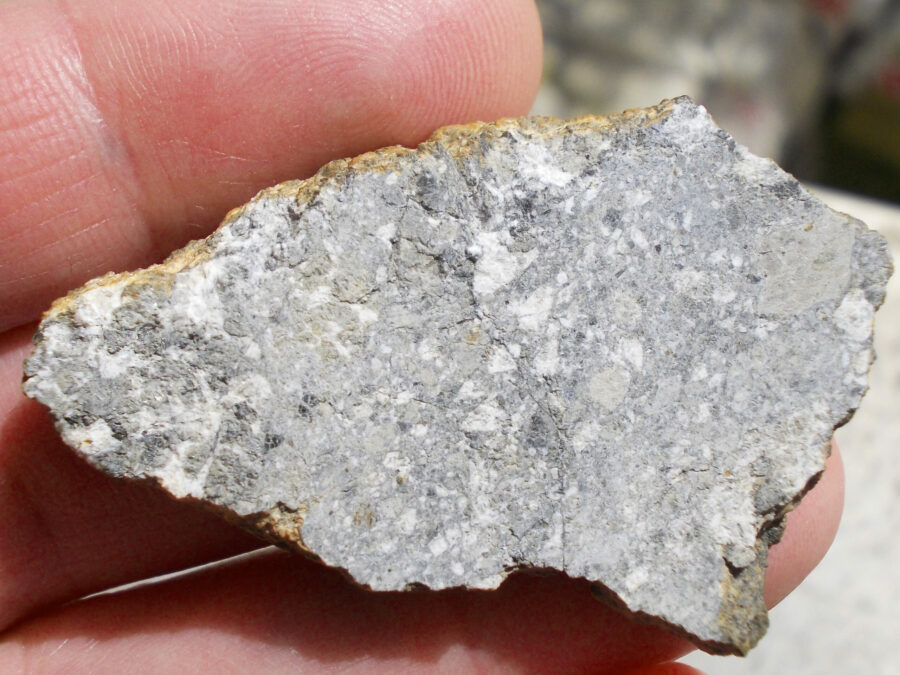
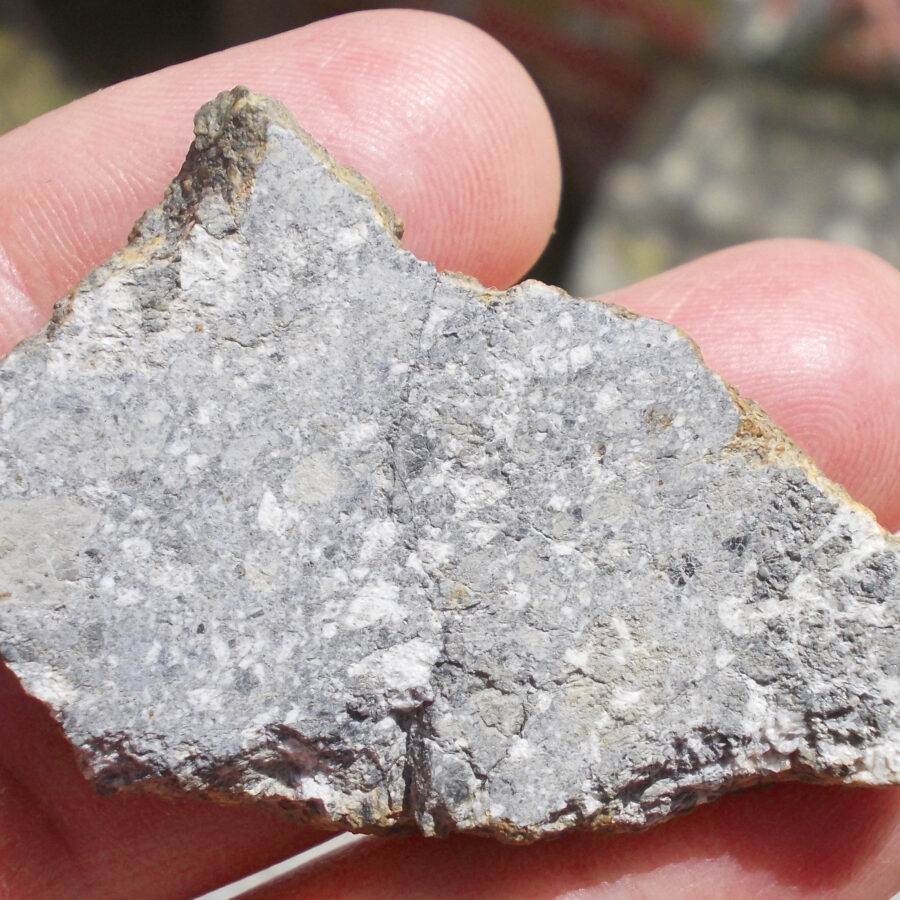
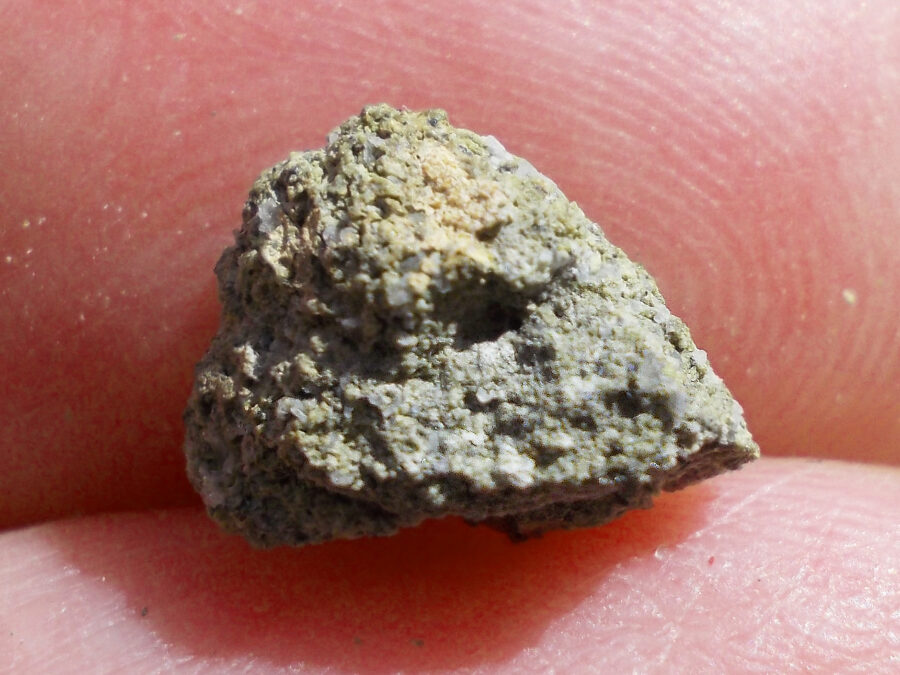
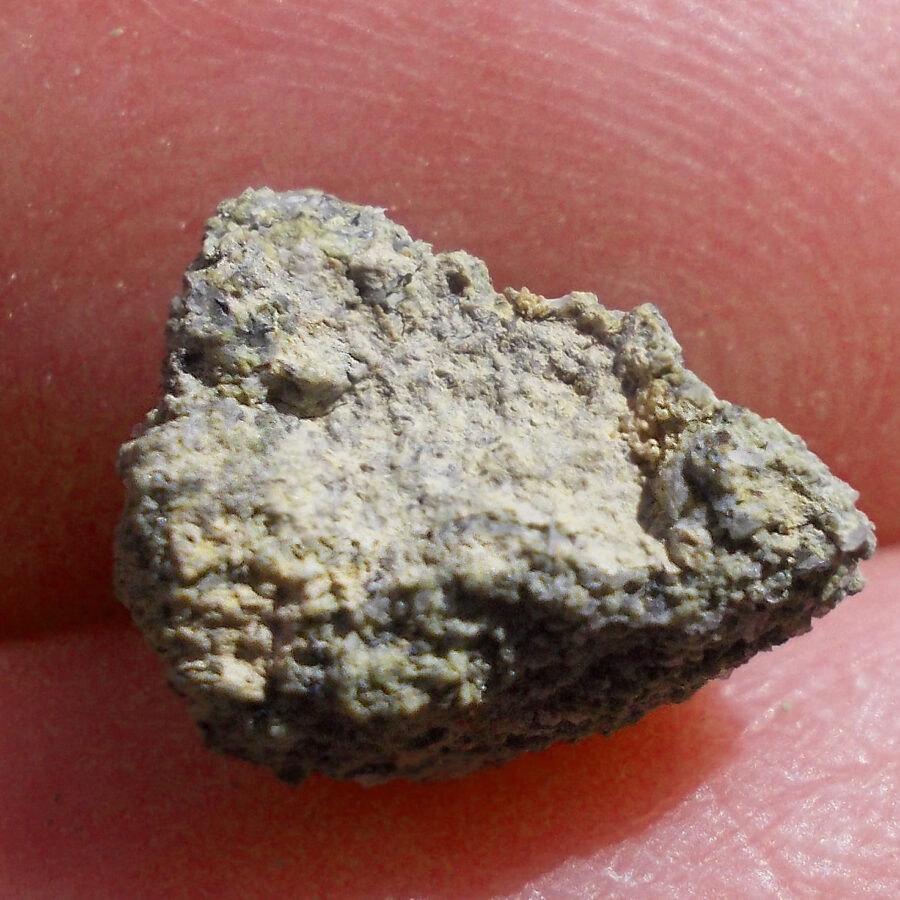
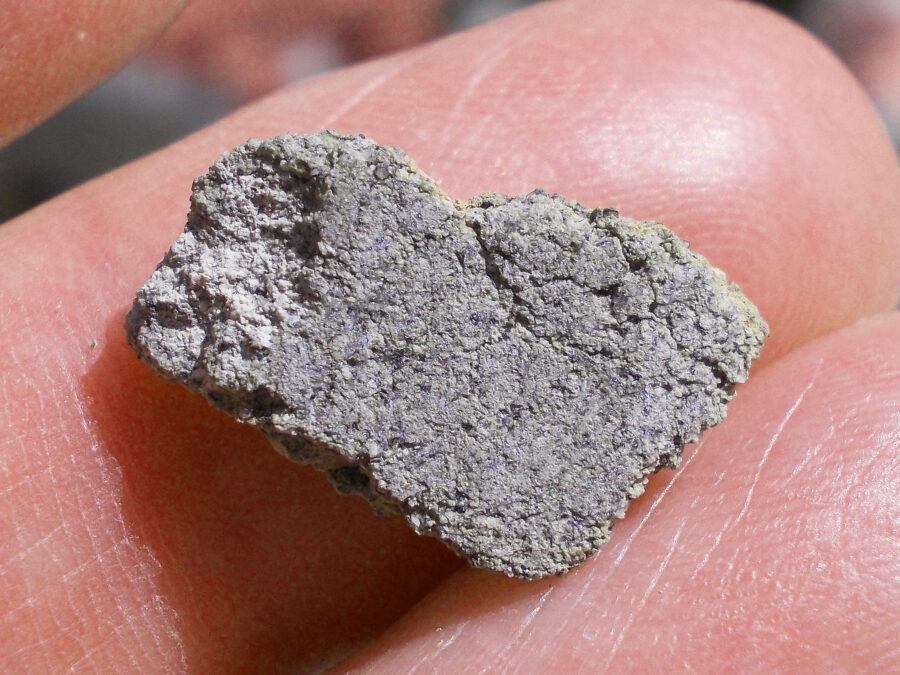
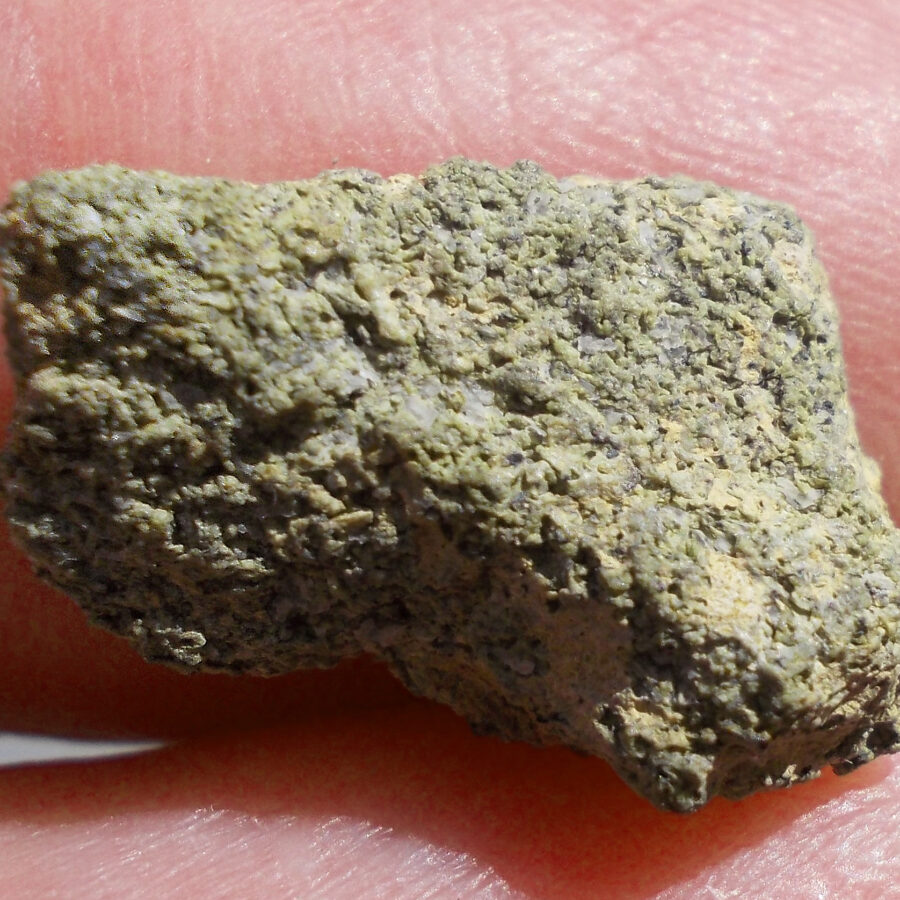
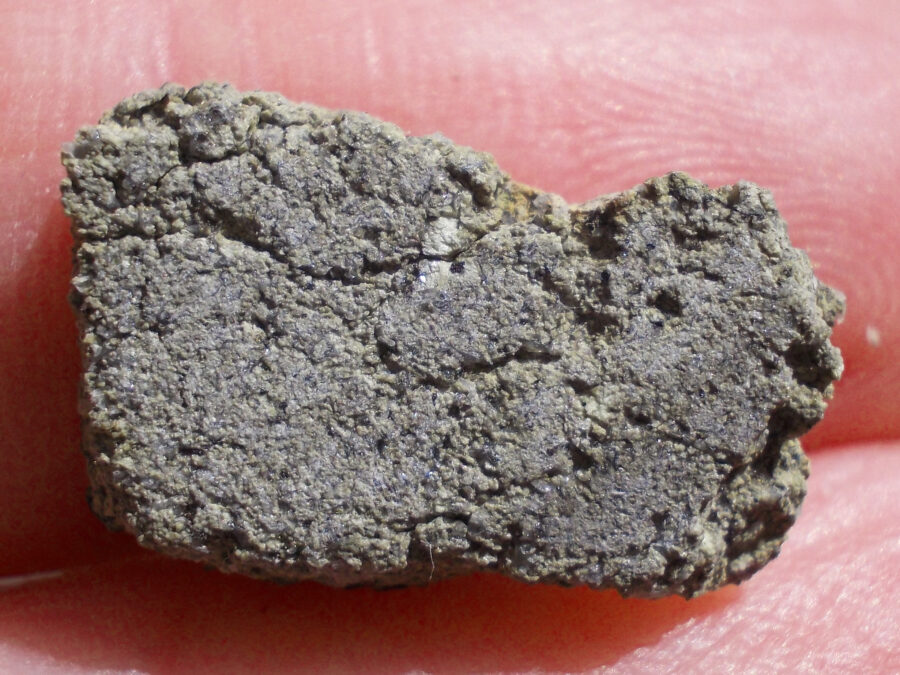
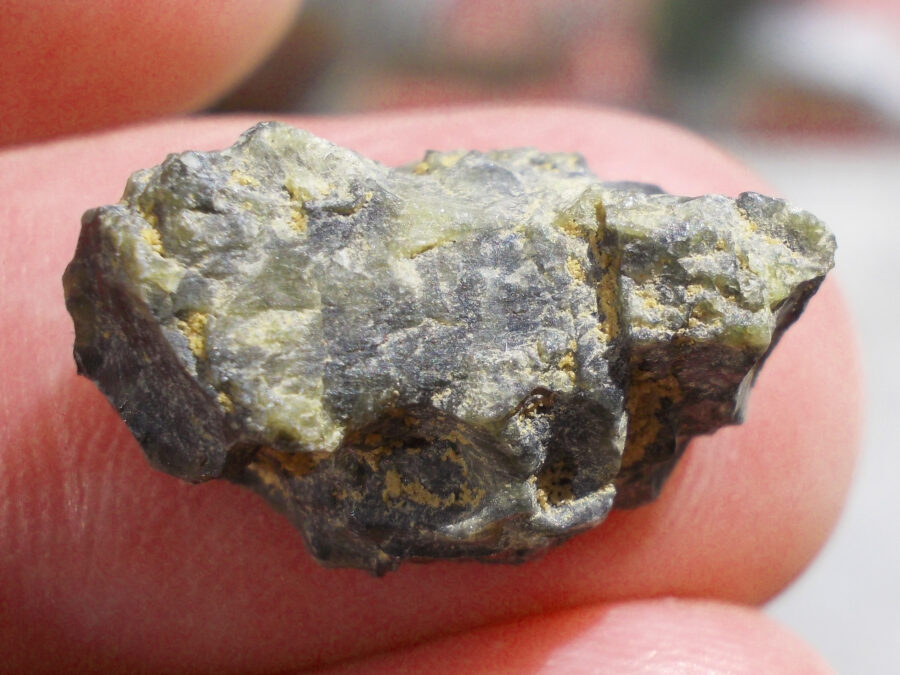
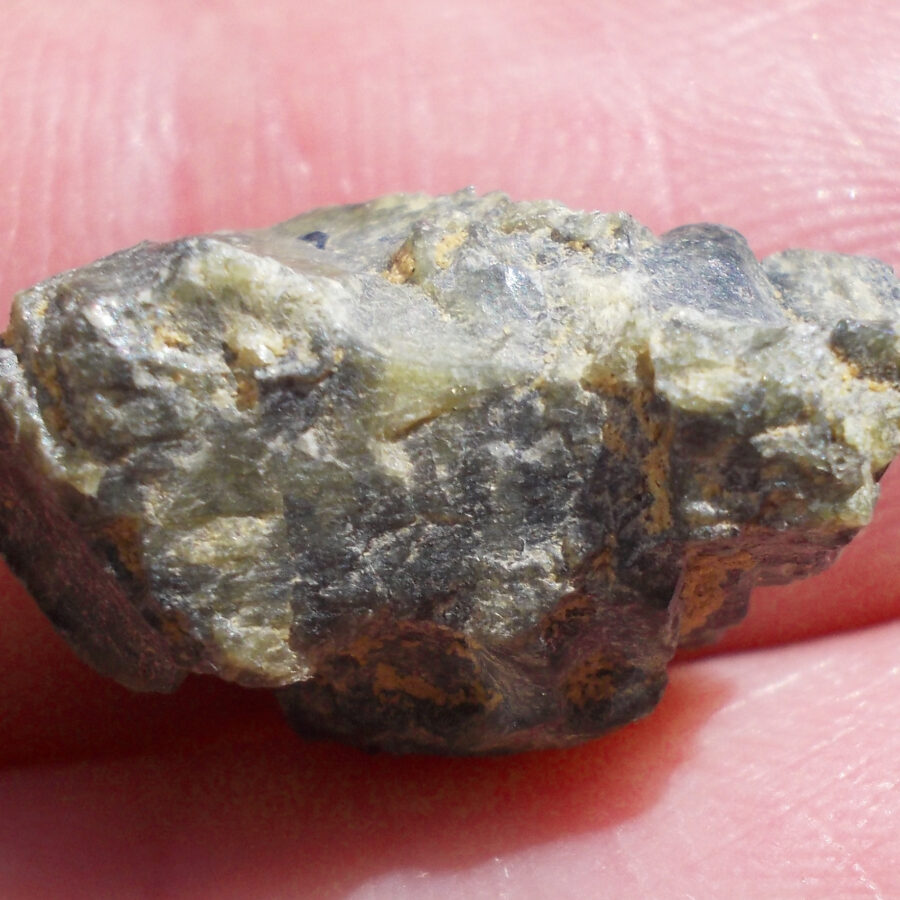
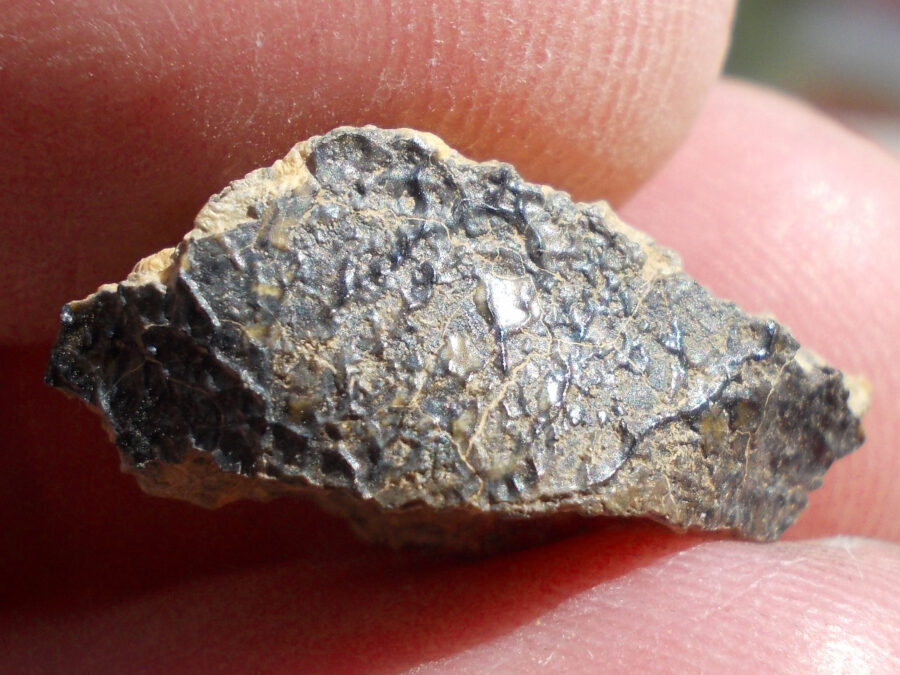
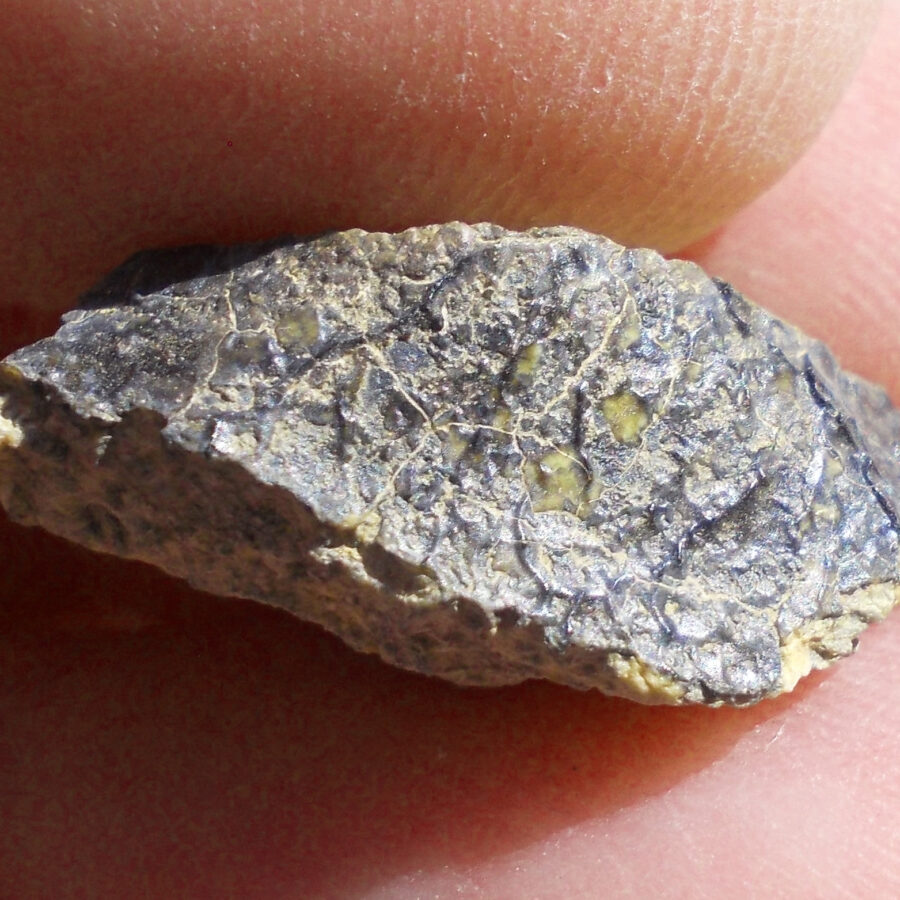
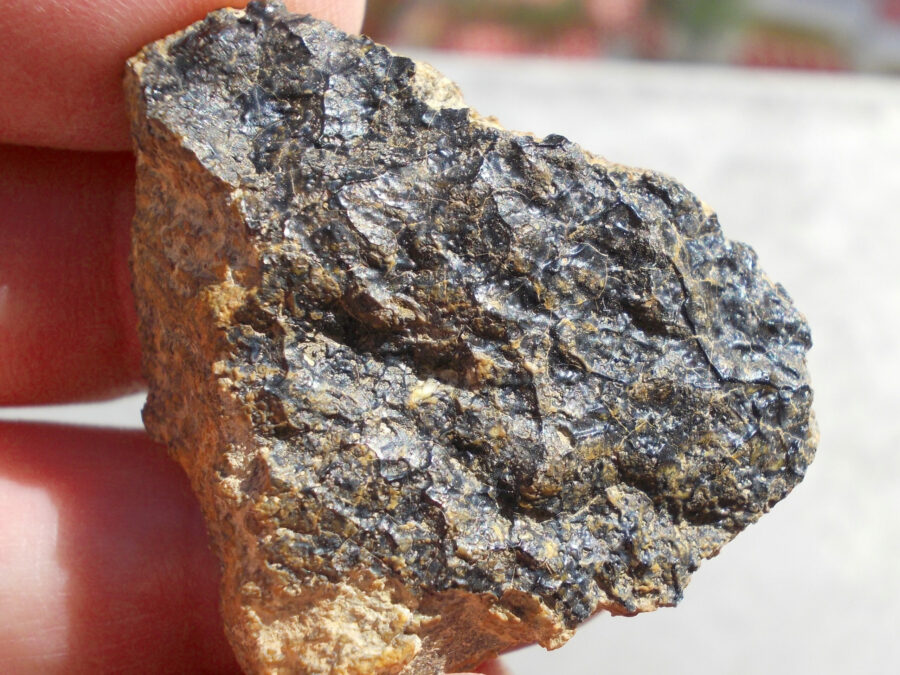
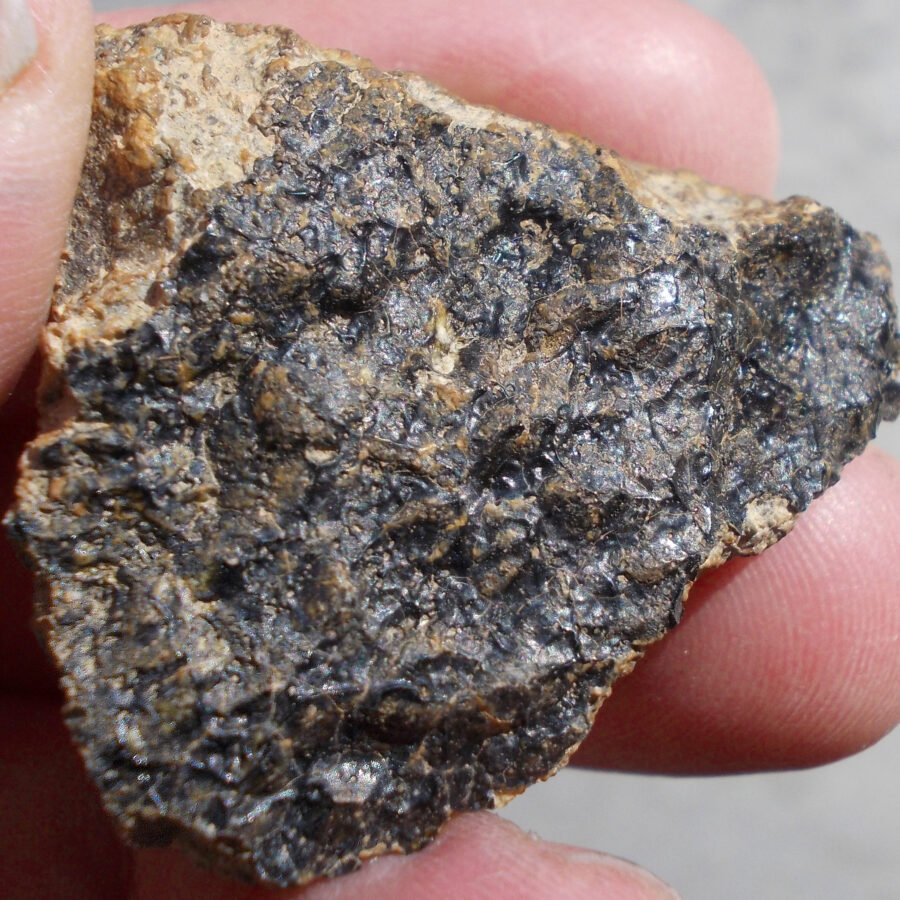
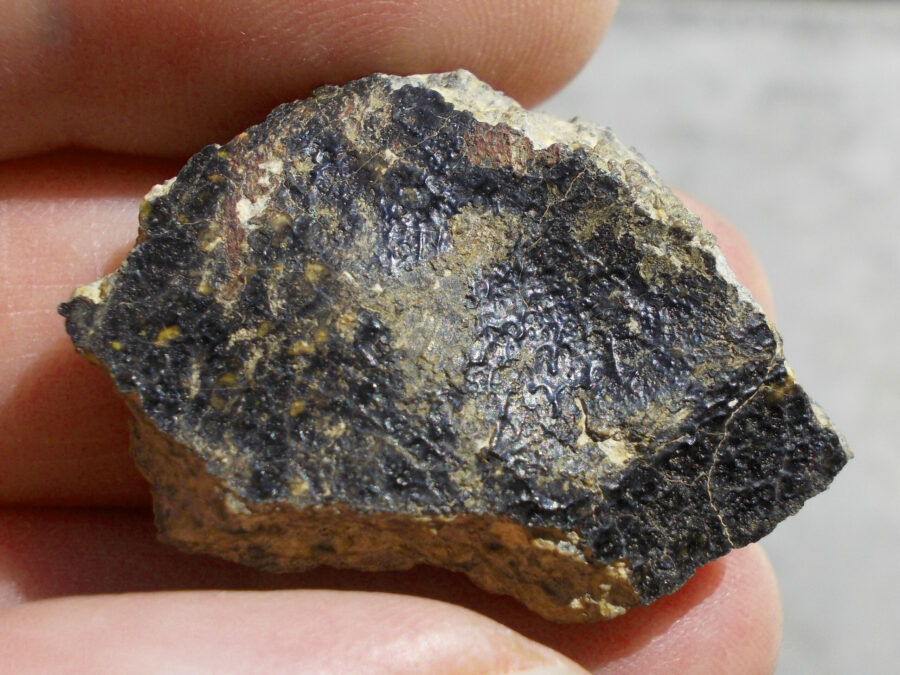
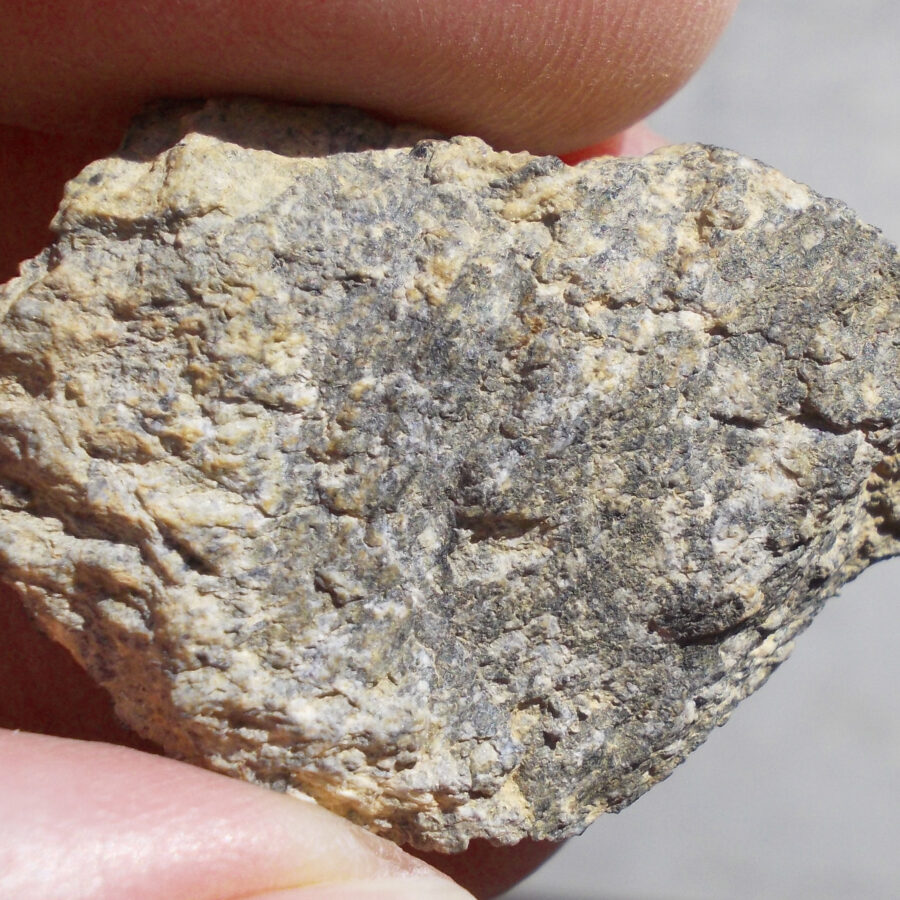
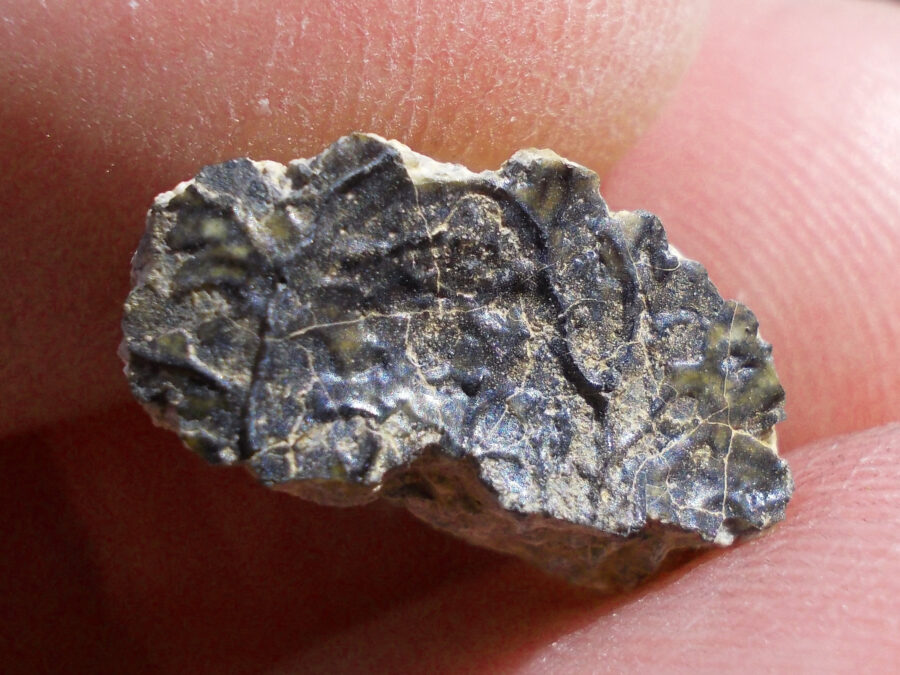
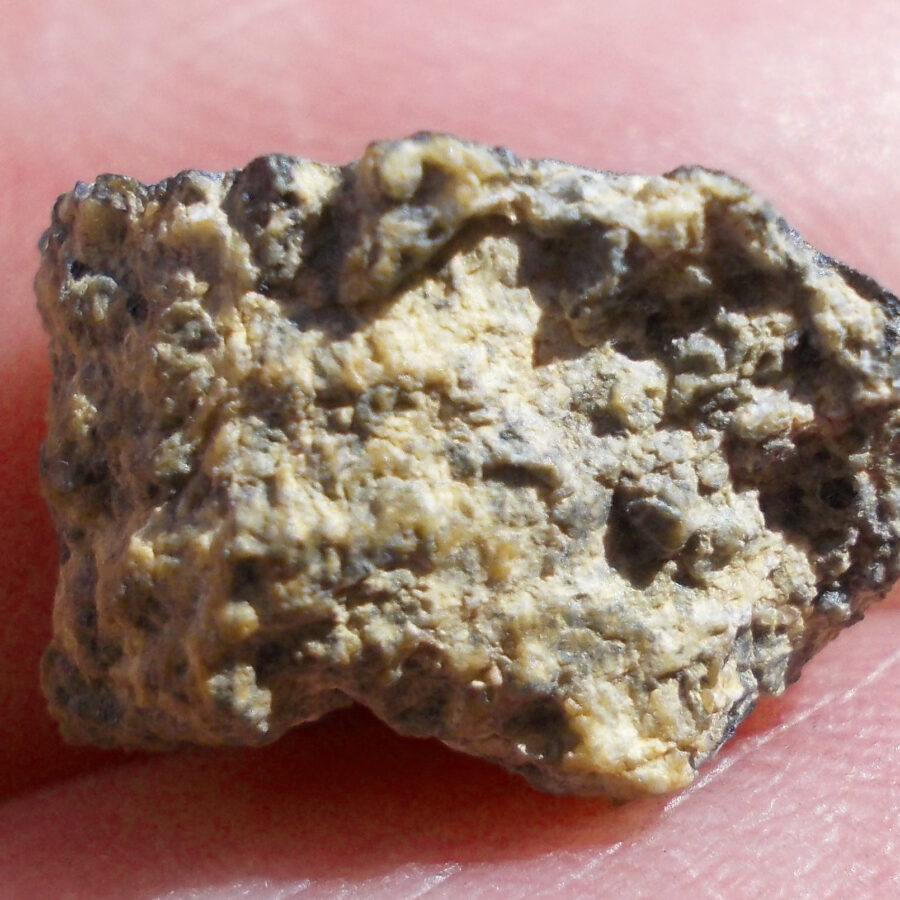
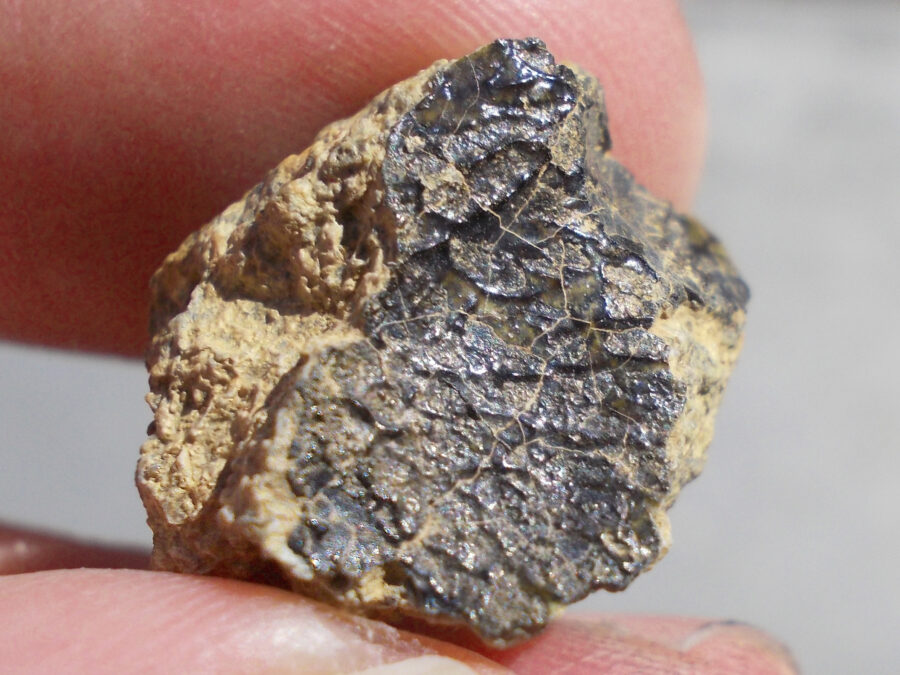
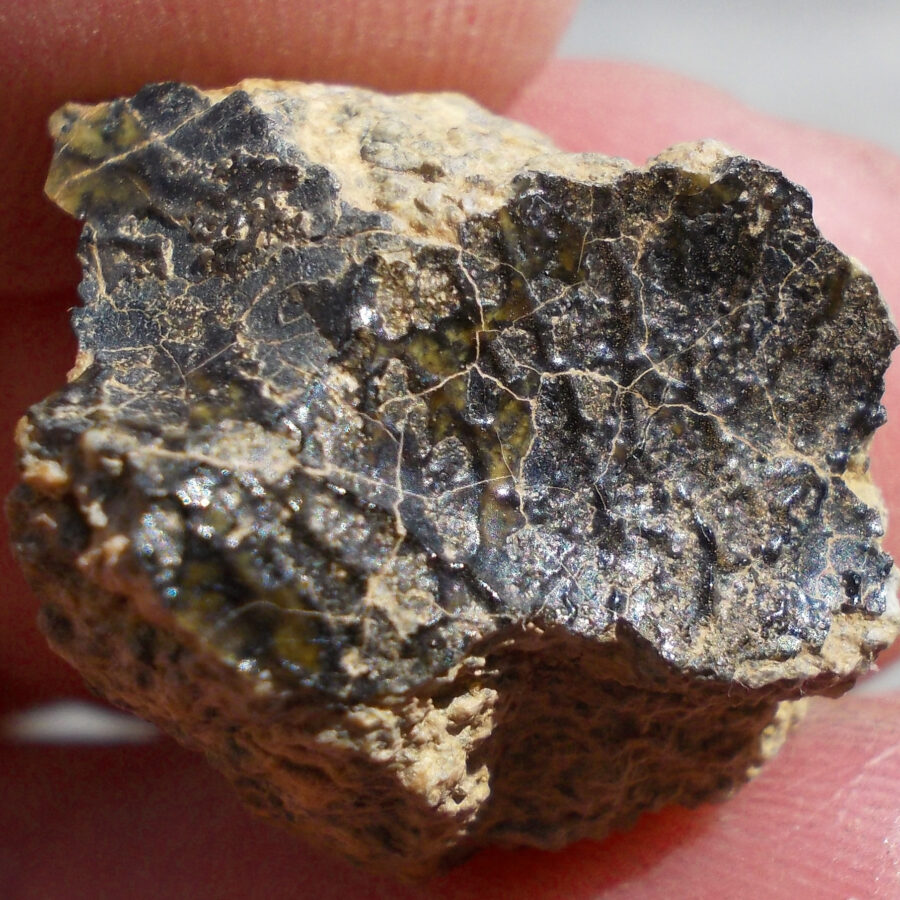
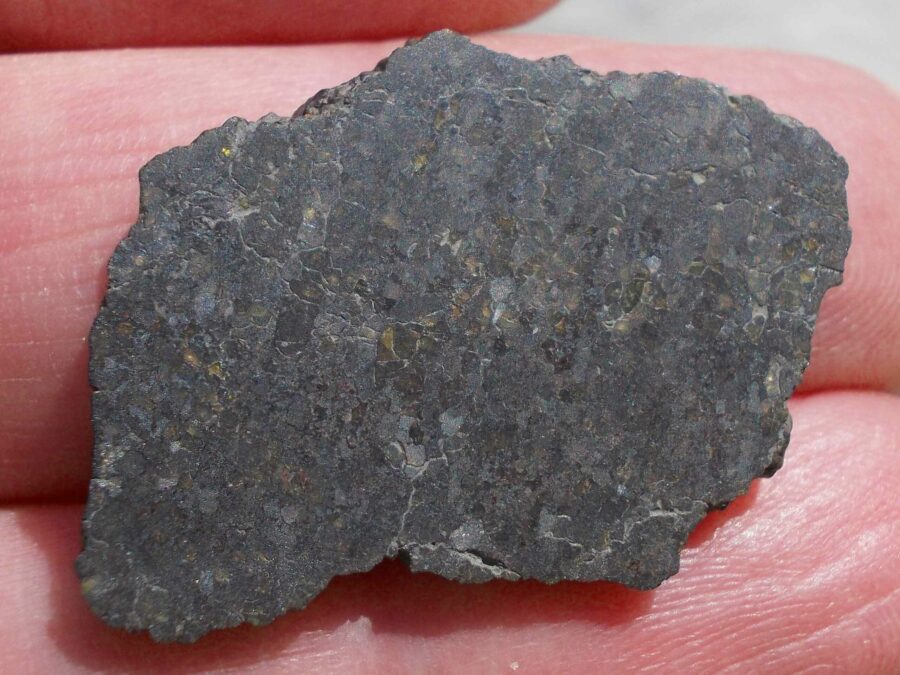
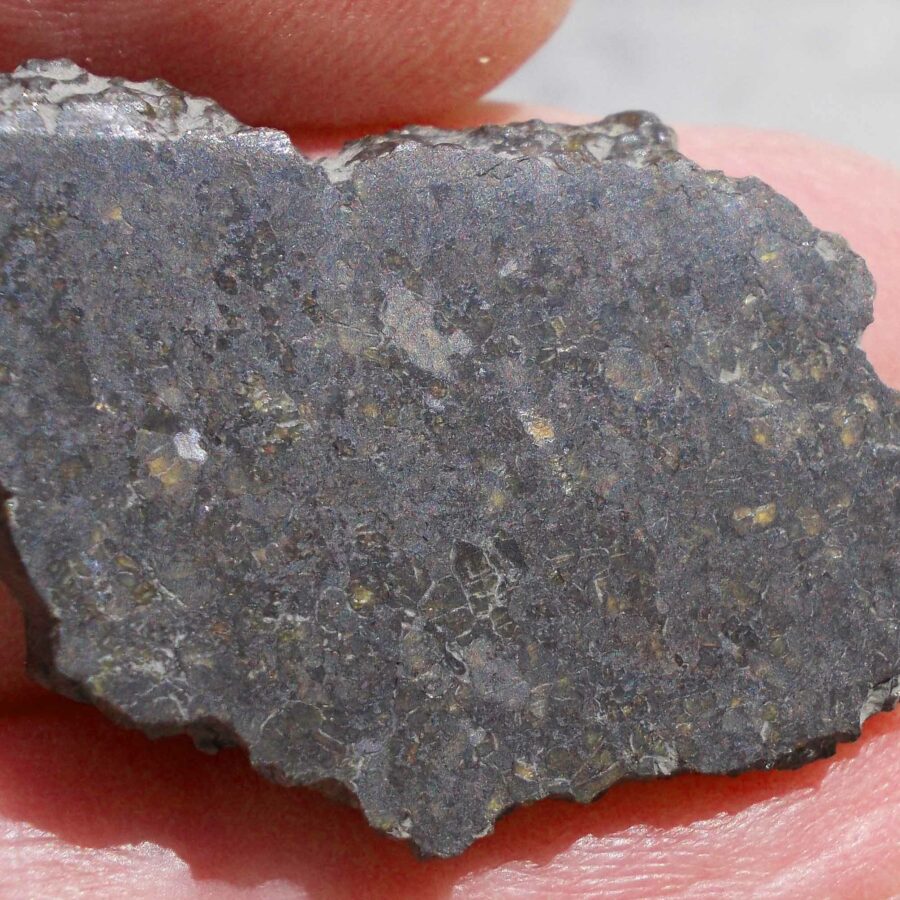
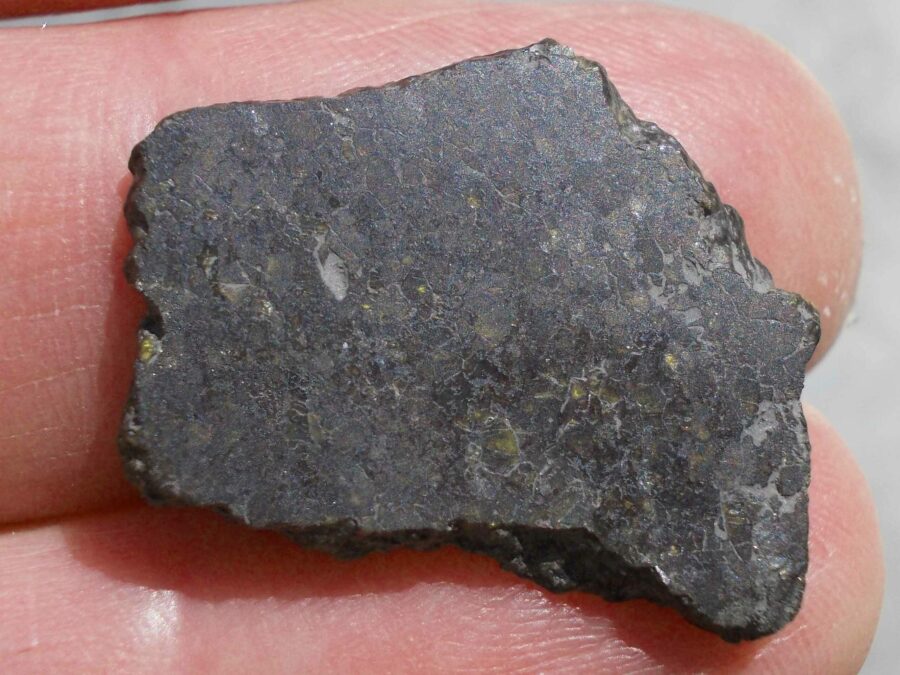
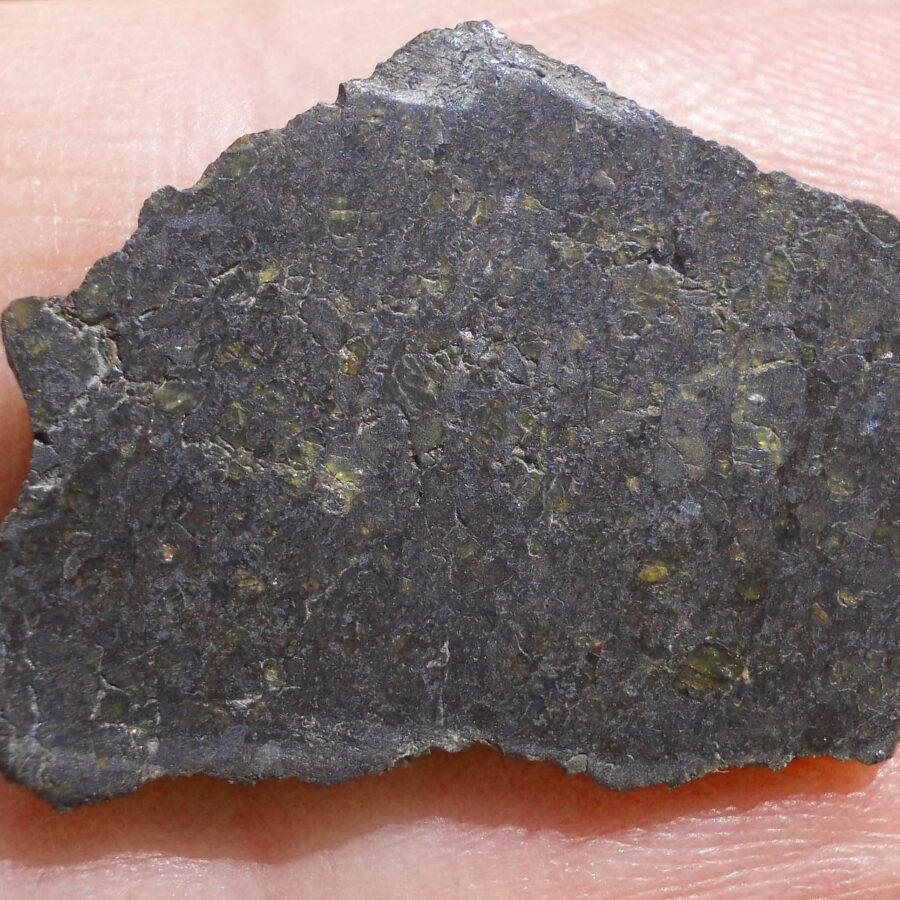
Zagora 006 Eucrite Brecciated #3 – 4,3 g
33,29 $Zagora 006 is a meteorite classified as brecciated eucrite of 1380 grams.
It was discovered near Zagora in Morocco by Ahmed Dich and Hssain Azmamar in January 2021.
The eucrites come from the Asteroid Vesta.
Writeup from MB 110 :
Zagora 006 30°18’46.21″N, 5°32’45.16″W
South, Morocco
Find: 2021 Jan
Classification: HED achondrite (Eucrite, brecciated)
History: Found by Ahmed Dich and Hssain Azmamar in January 2021. Bought by Jean Redelsperger from Zaid Oualguirah in February 2021.
Physical characteristics: Partially crusted stone with a light grey interior
Petrography: (J. Gattacceca, CEREGE) Brecciated igneous rock with mineral and lithic gabbroic clasts. Main minerals are pyroxene (some exsolved) and plagioclase with grain size in the 100 to 500 µm range. Accessory minerals: metal (to 150 µm), chromite (to 100 µm), ilmenite (to 150 µm), troilite (to 200 µm).
Geochemistry: Low-Ca pyroxene Fs50.7Wo3.8, Fs48.5Wo6.4. Ca-pyroxene Fs38.8Wo20.5, Fs23.0Wo41.3, Fs23.3Wo41.4. Pyroxene FeO/MnO 31.8±1.4 (n=5). Plagioclase An92.5Ab7.3Or0.2, An80.2Ab18.8Or0.9.
Classification: Achondrite (eucrite, brecciated)
Specimens: 22 g type specimen at CEREGE. Main mass with Jean Redelsperger