Affichage de 253–270 sur 1901 résultatsTrié du plus récent au plus ancien
170,00€
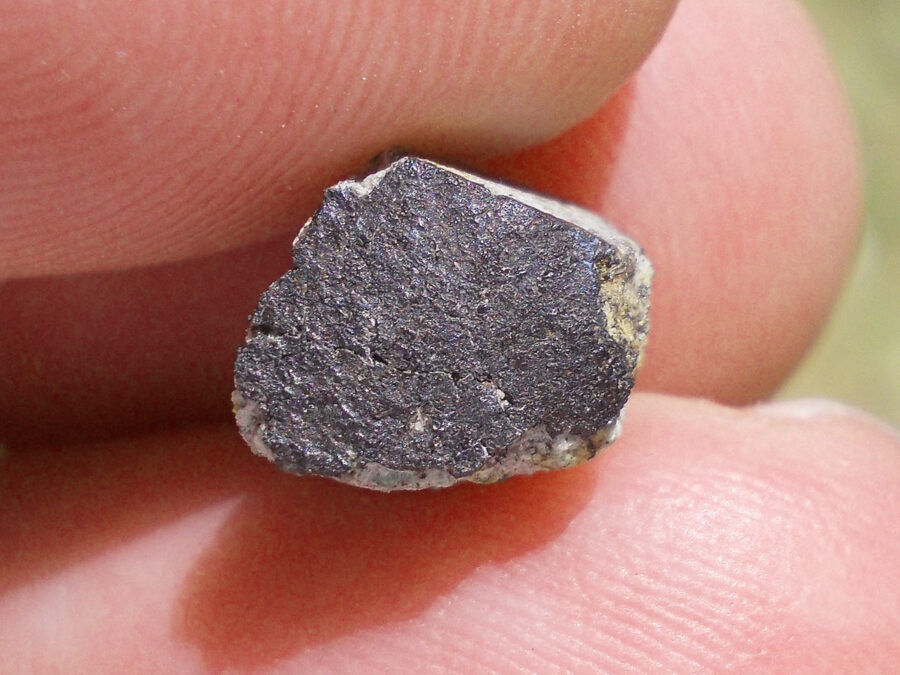
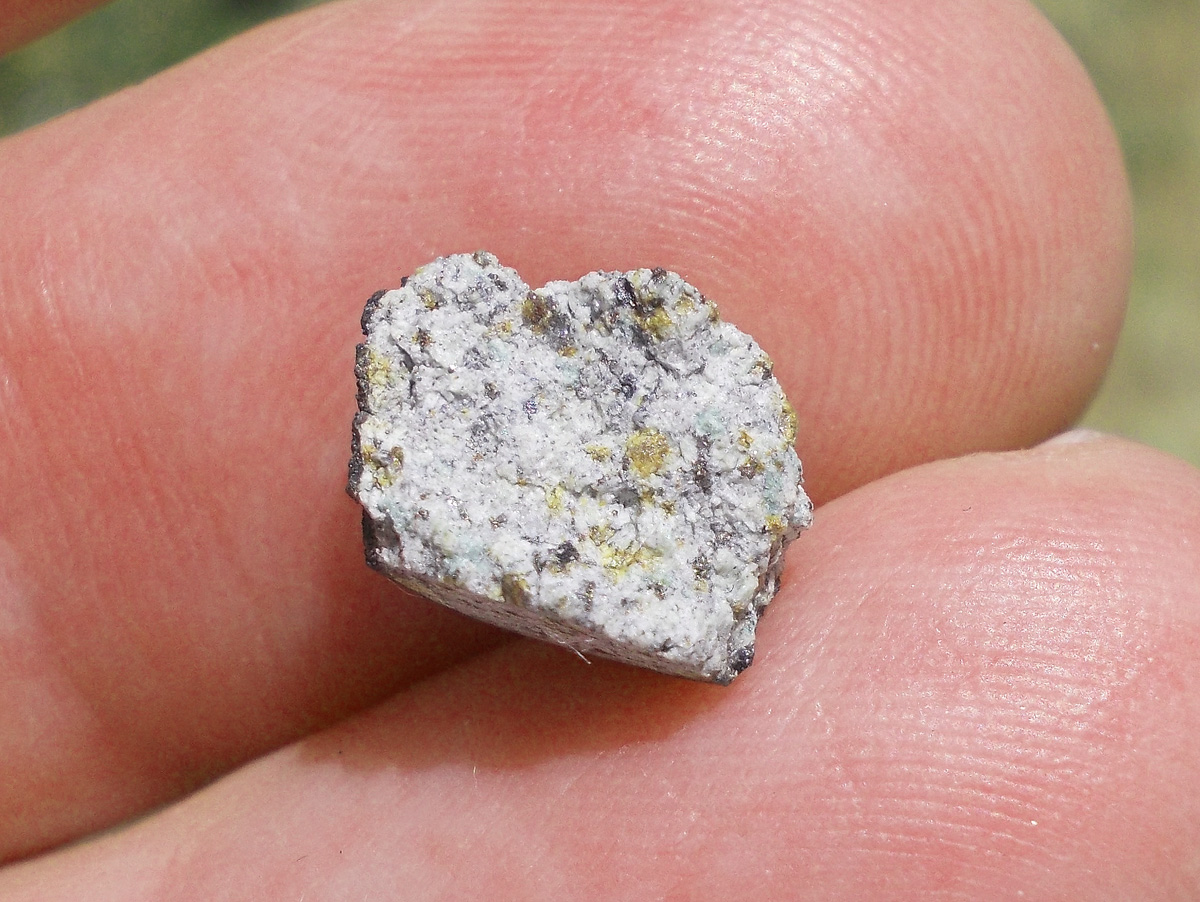
La météorite de Katol est tombée en Inde en 2012.
La masse totale récupérée est supérieure à 13 kg.
Une étude rapporte pour la première fois la présence de veines du minéral bridgmanite dans l’échantillon de météorite.
La bridgmanite est le minéral le plus abondant en volume à l’intérieur de la Terre.
36,00€
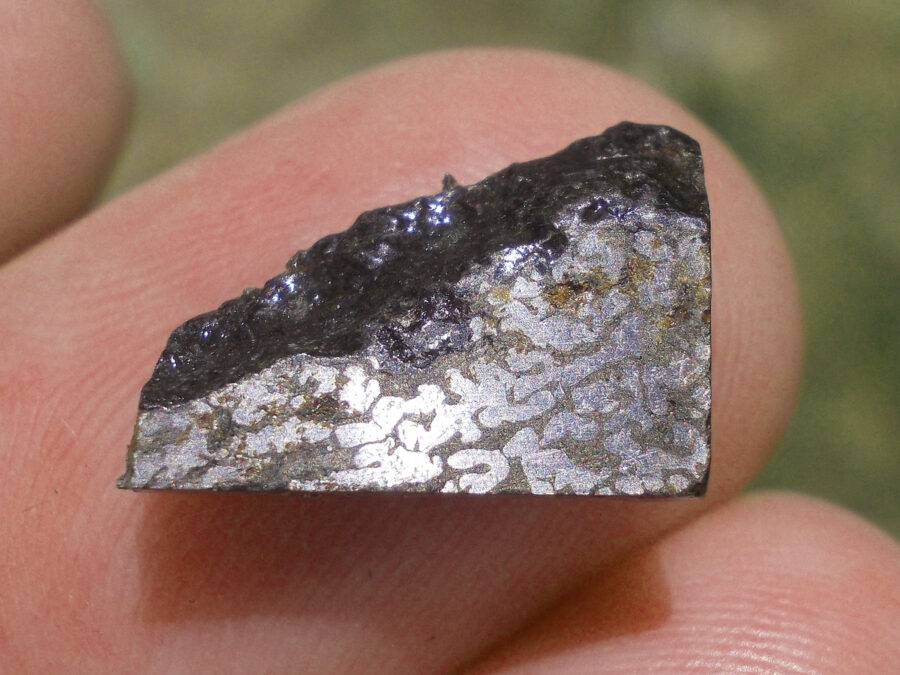
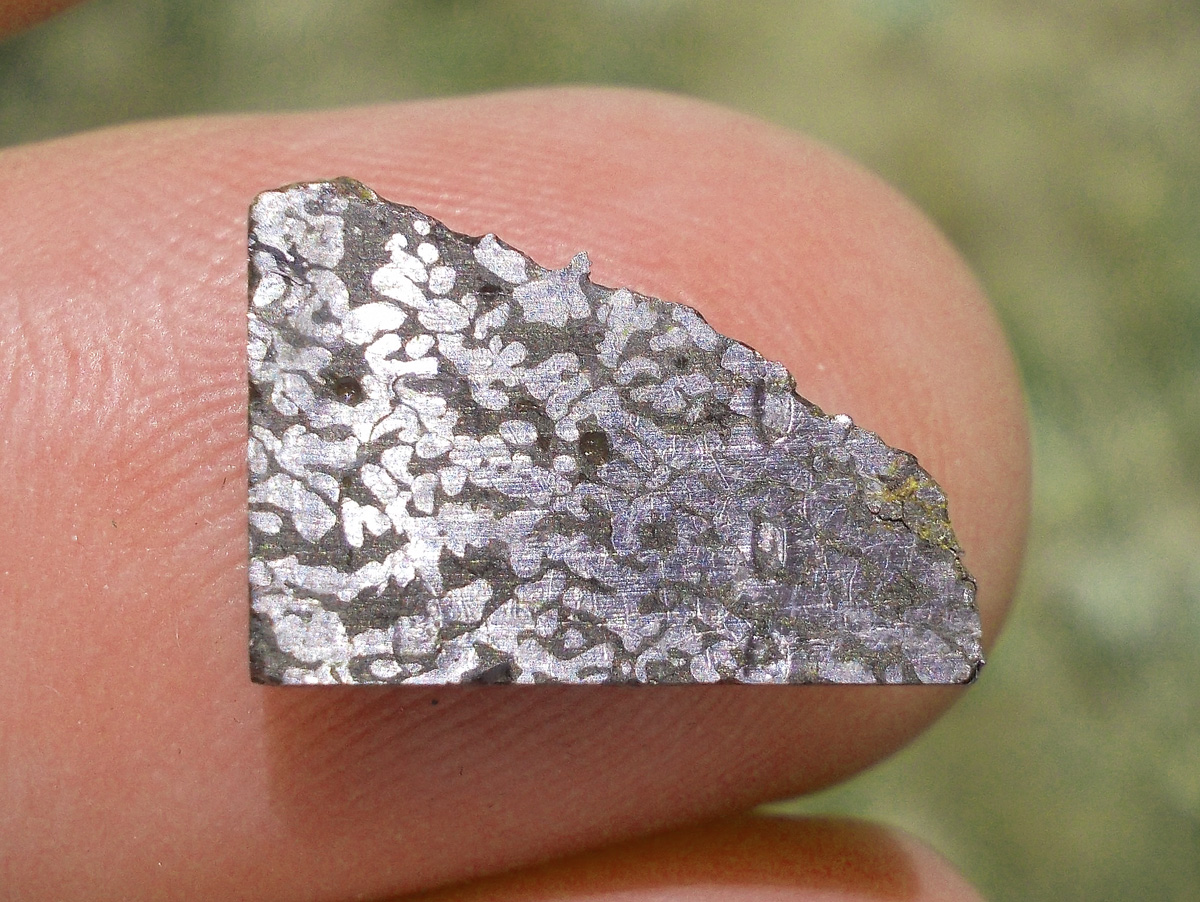
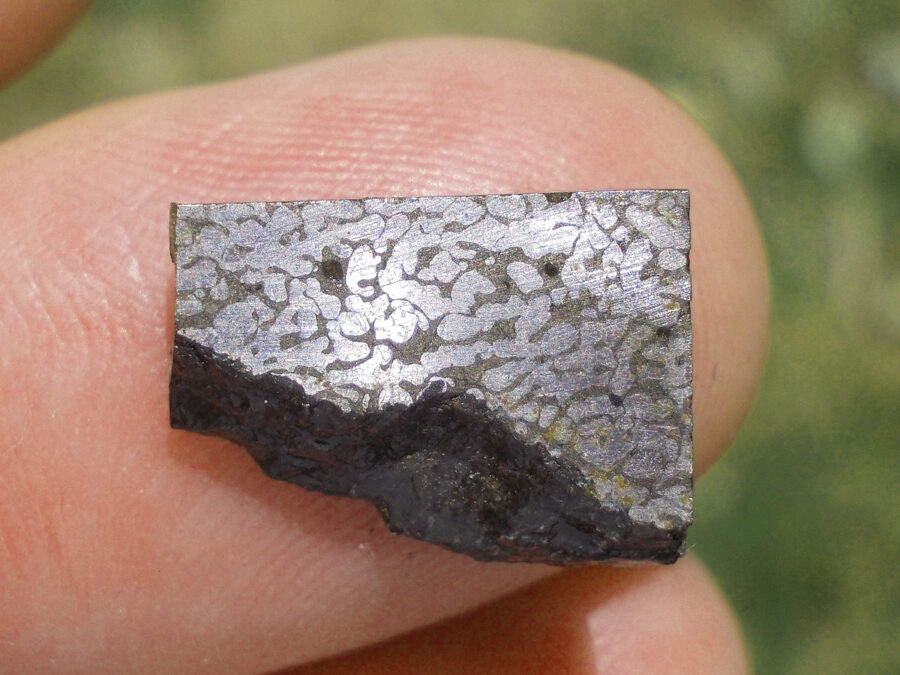
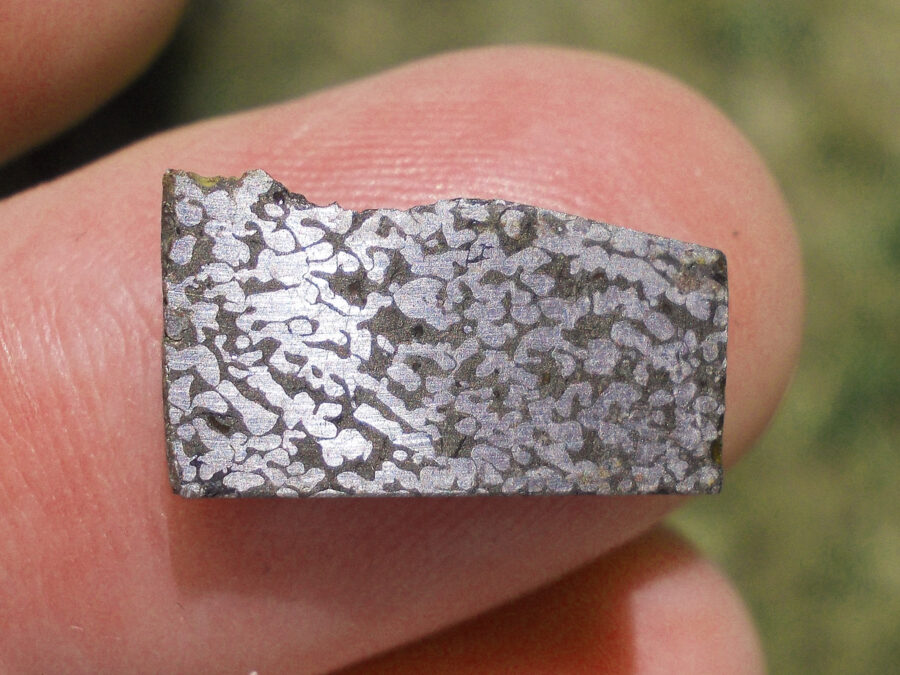
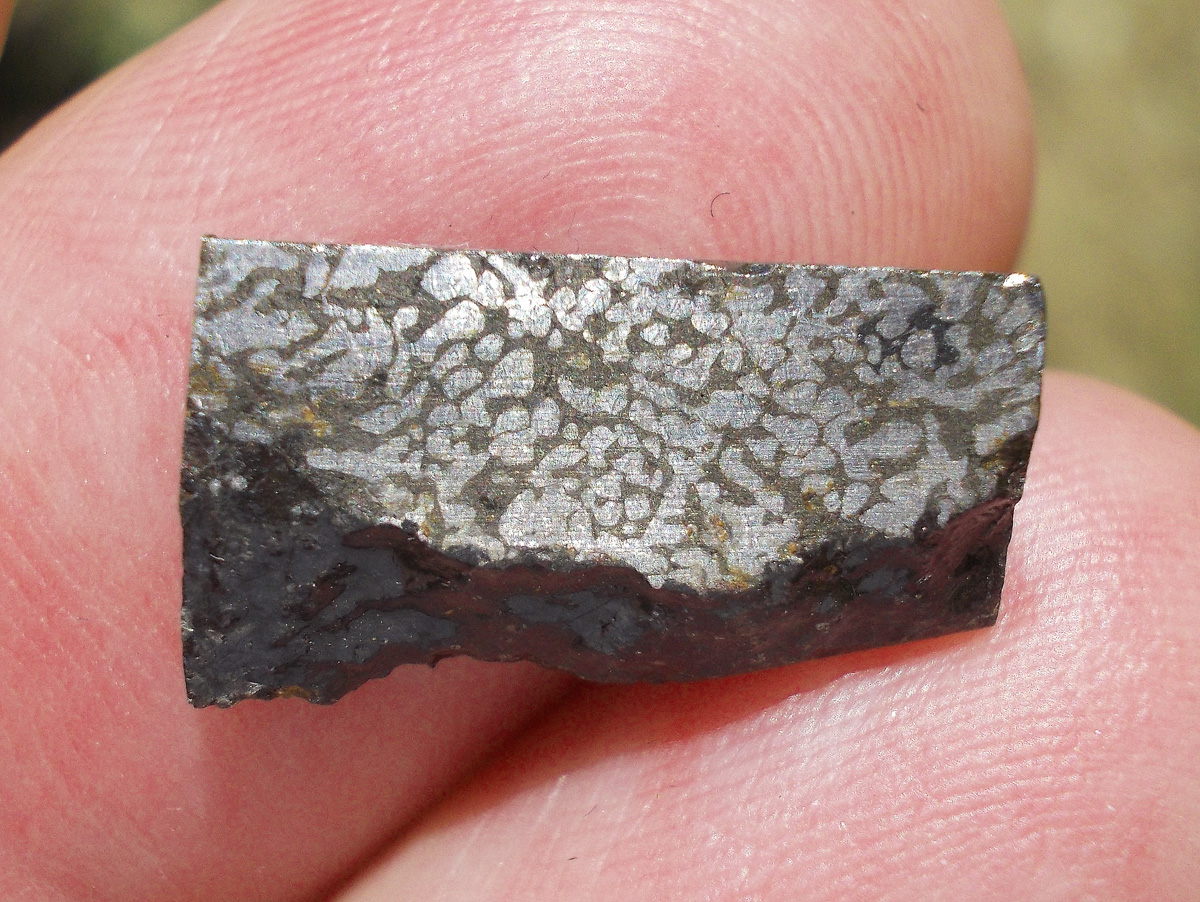
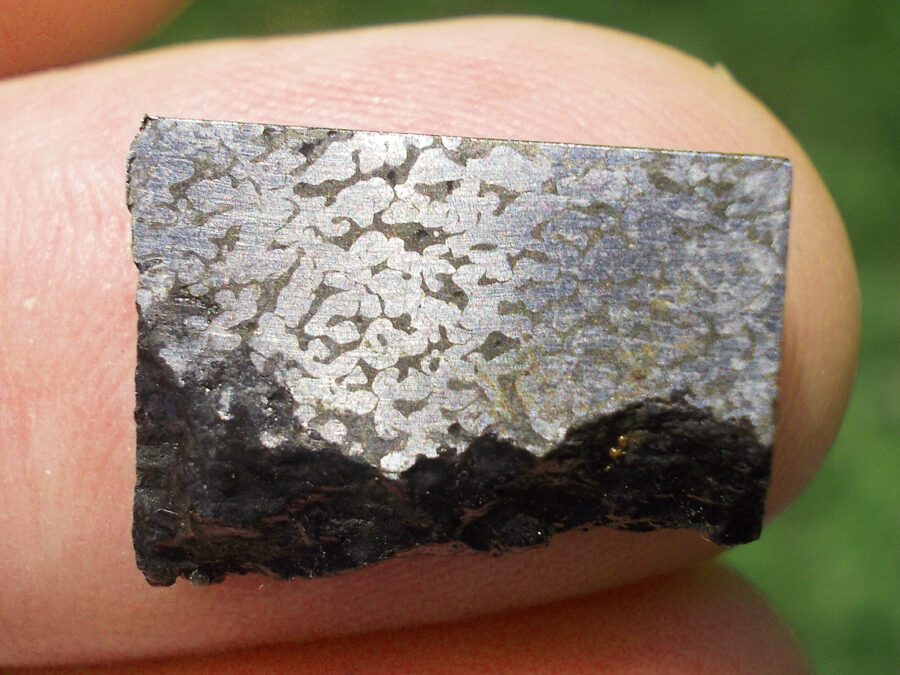
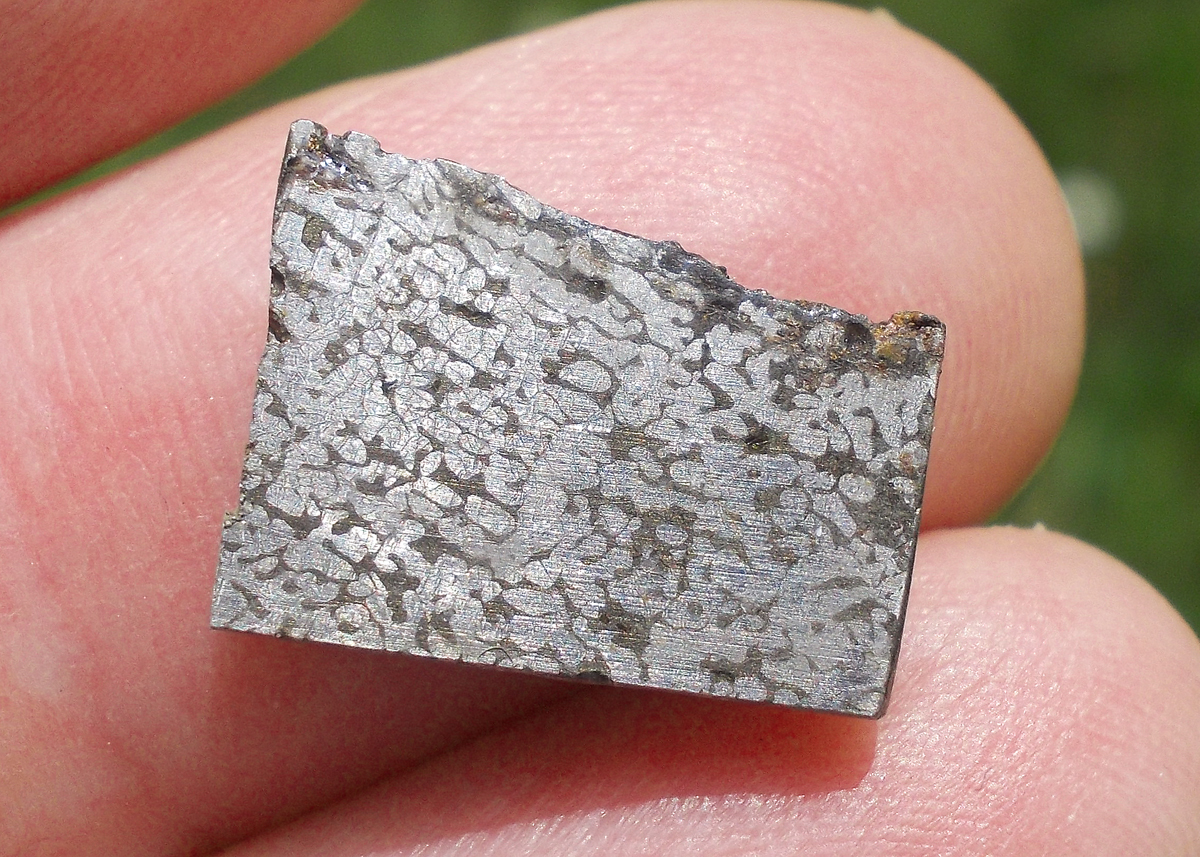
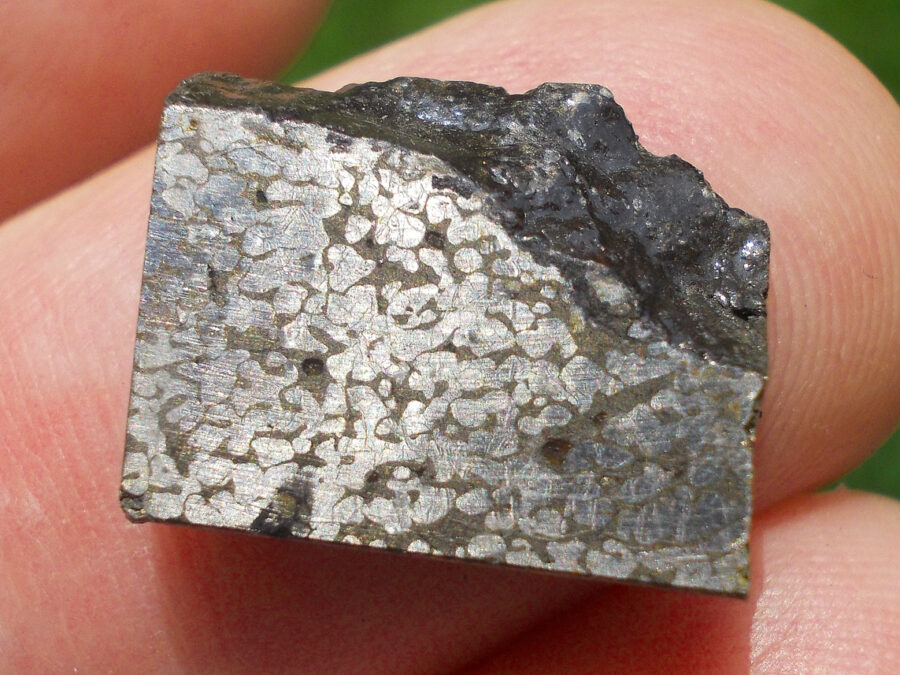
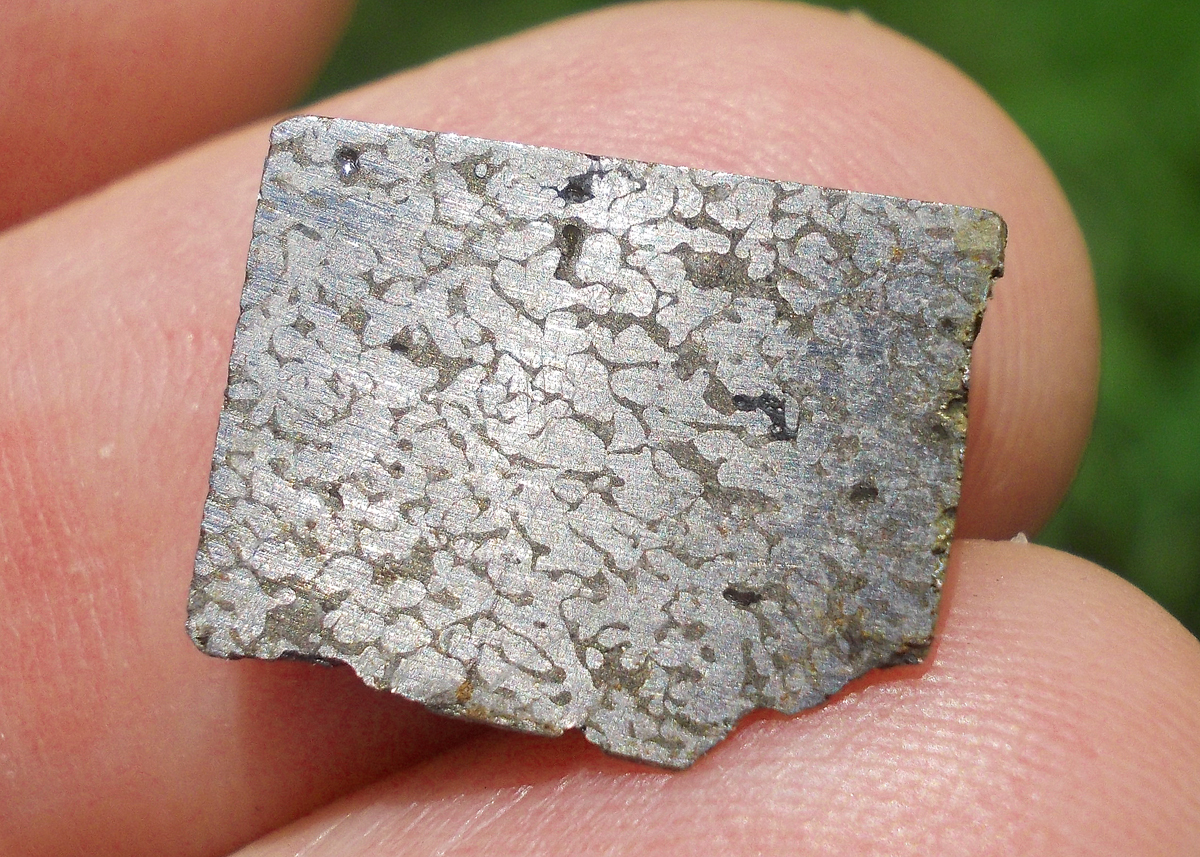
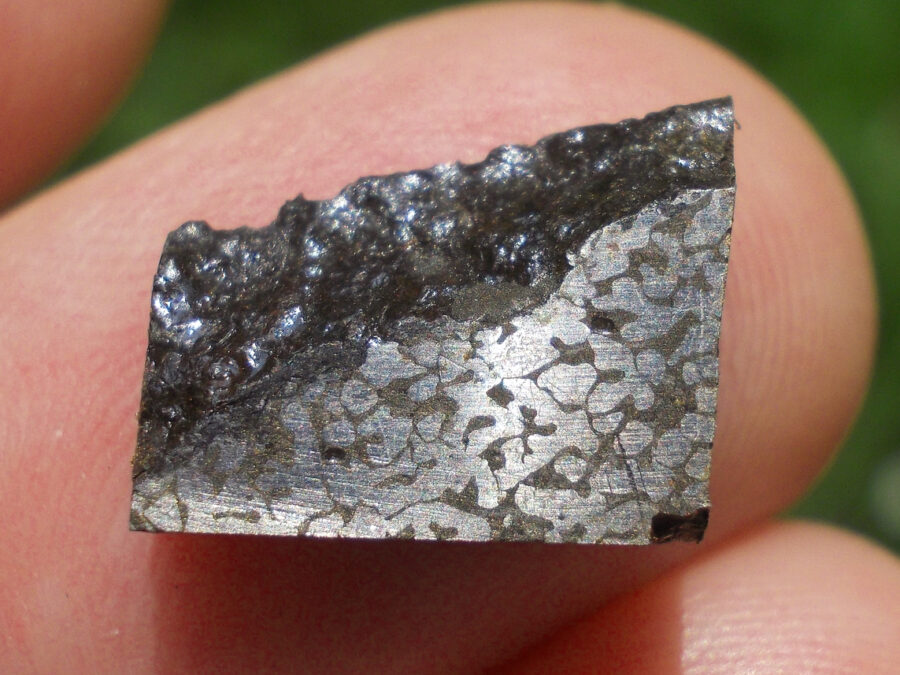
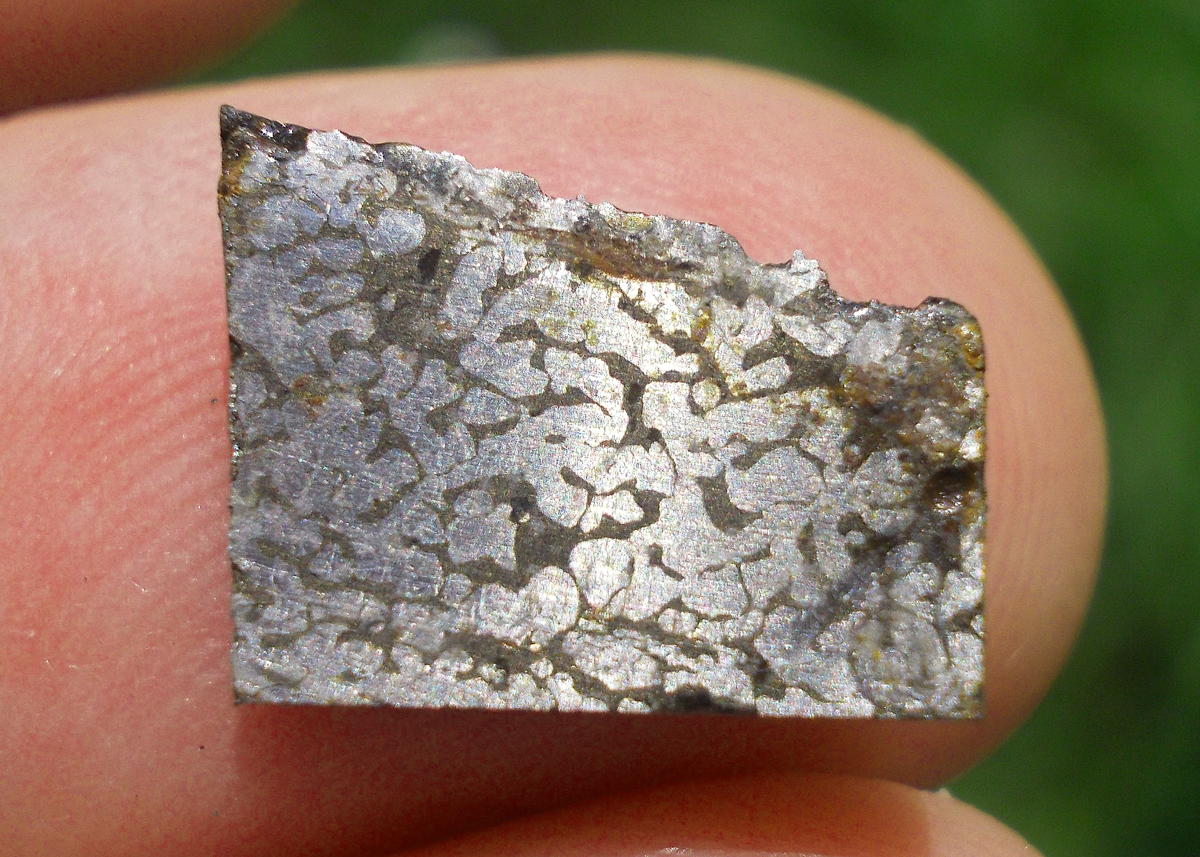
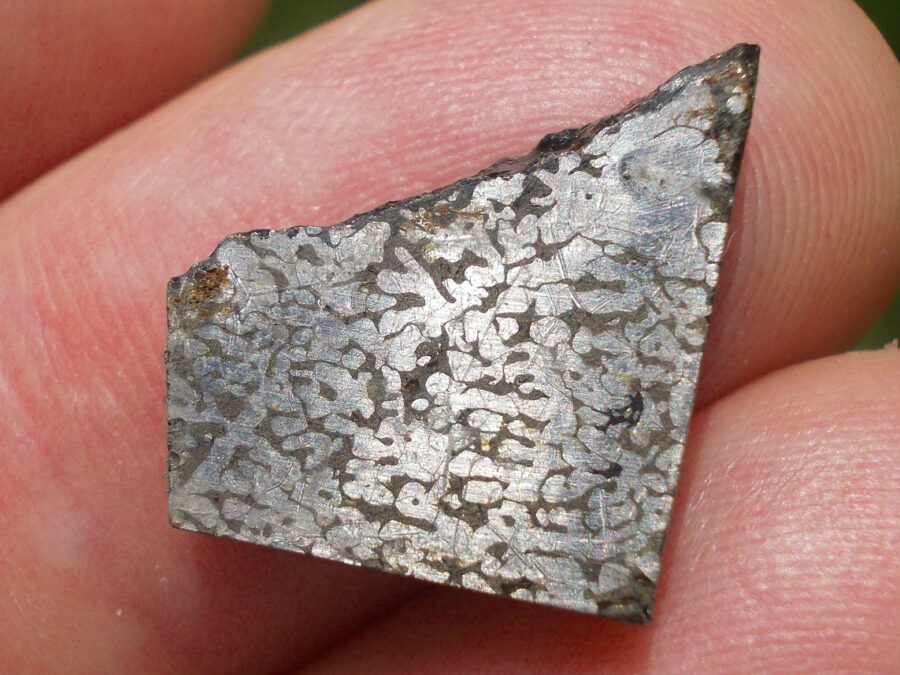
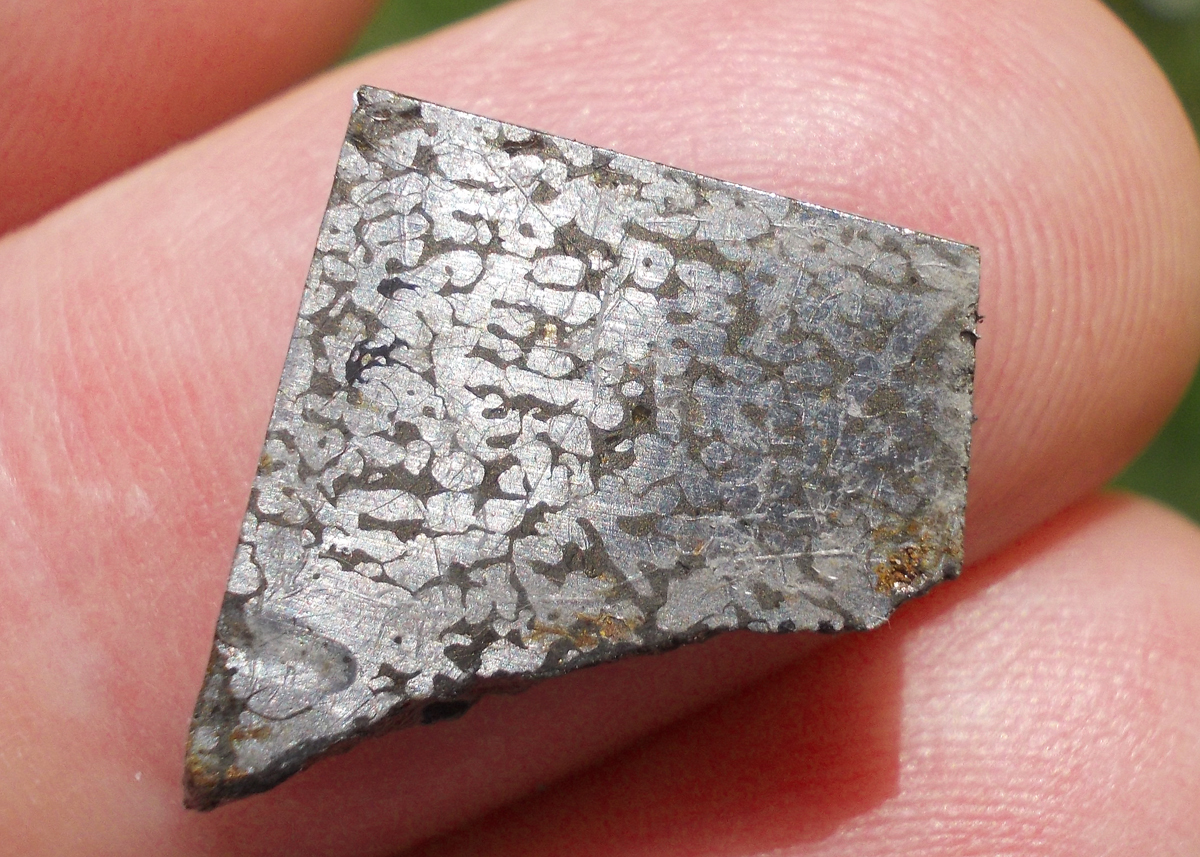
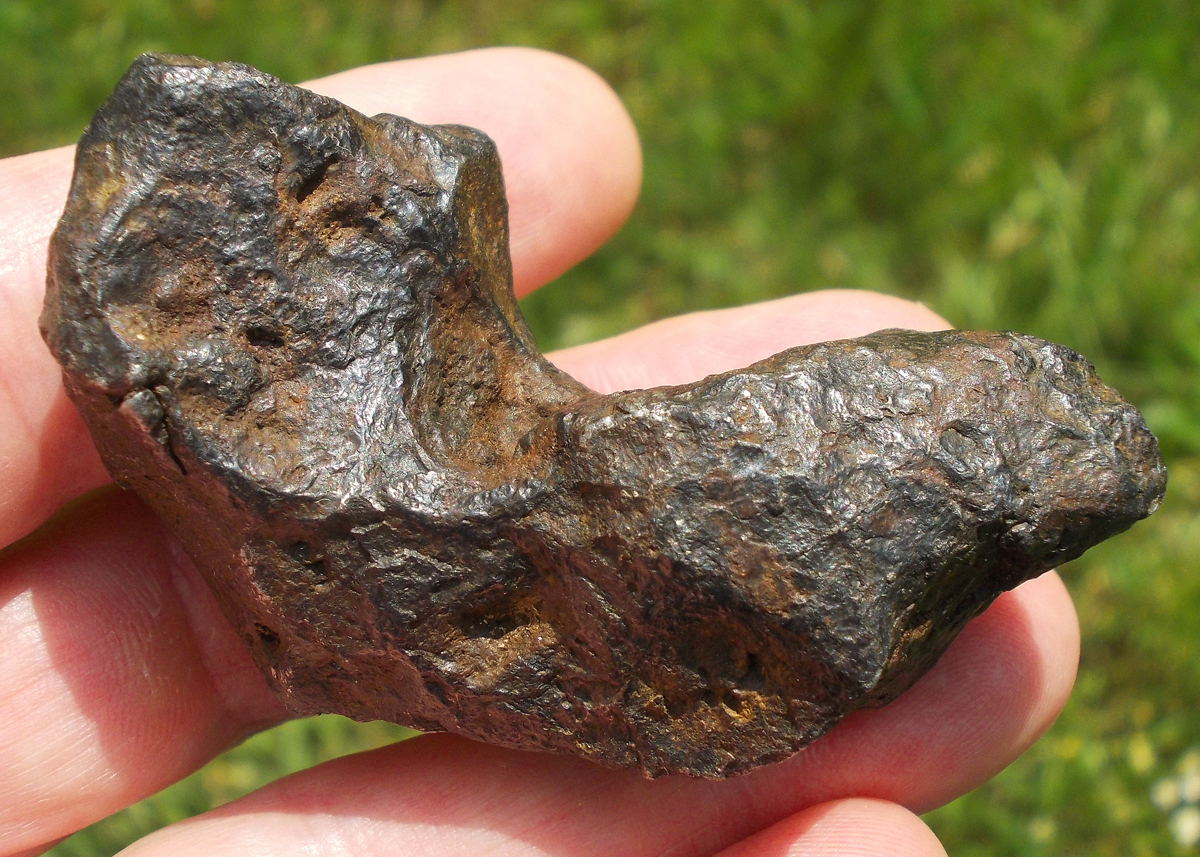
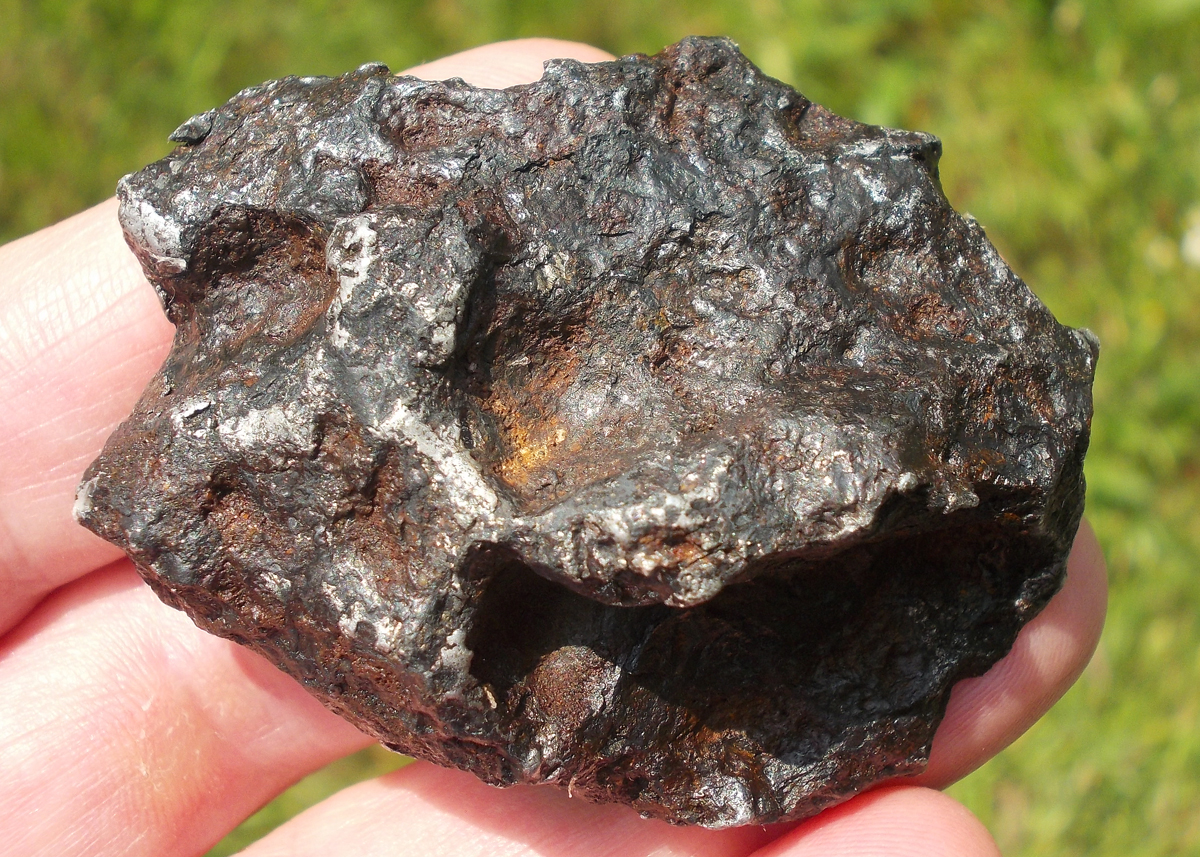
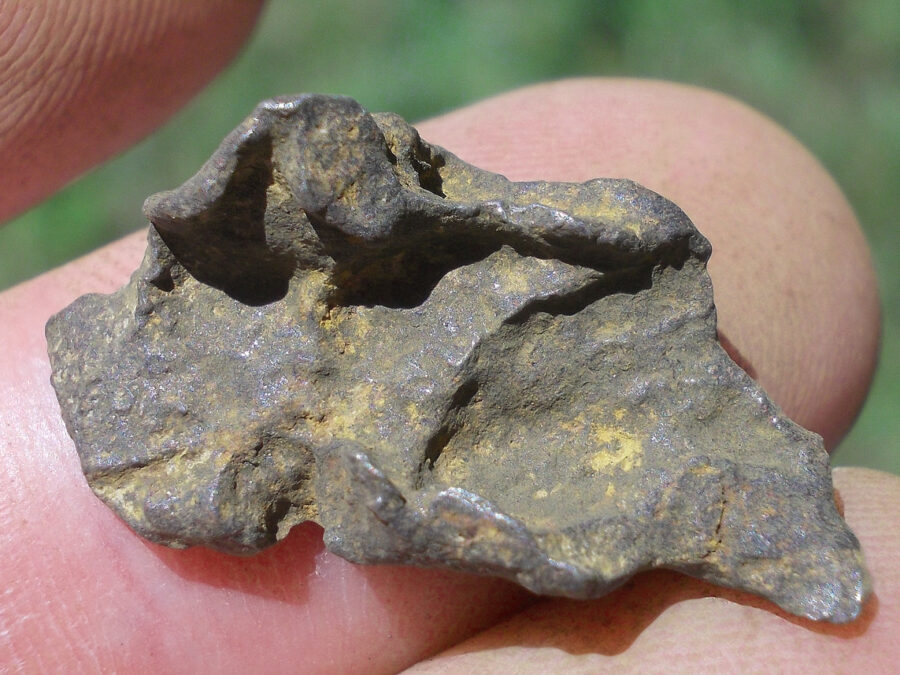
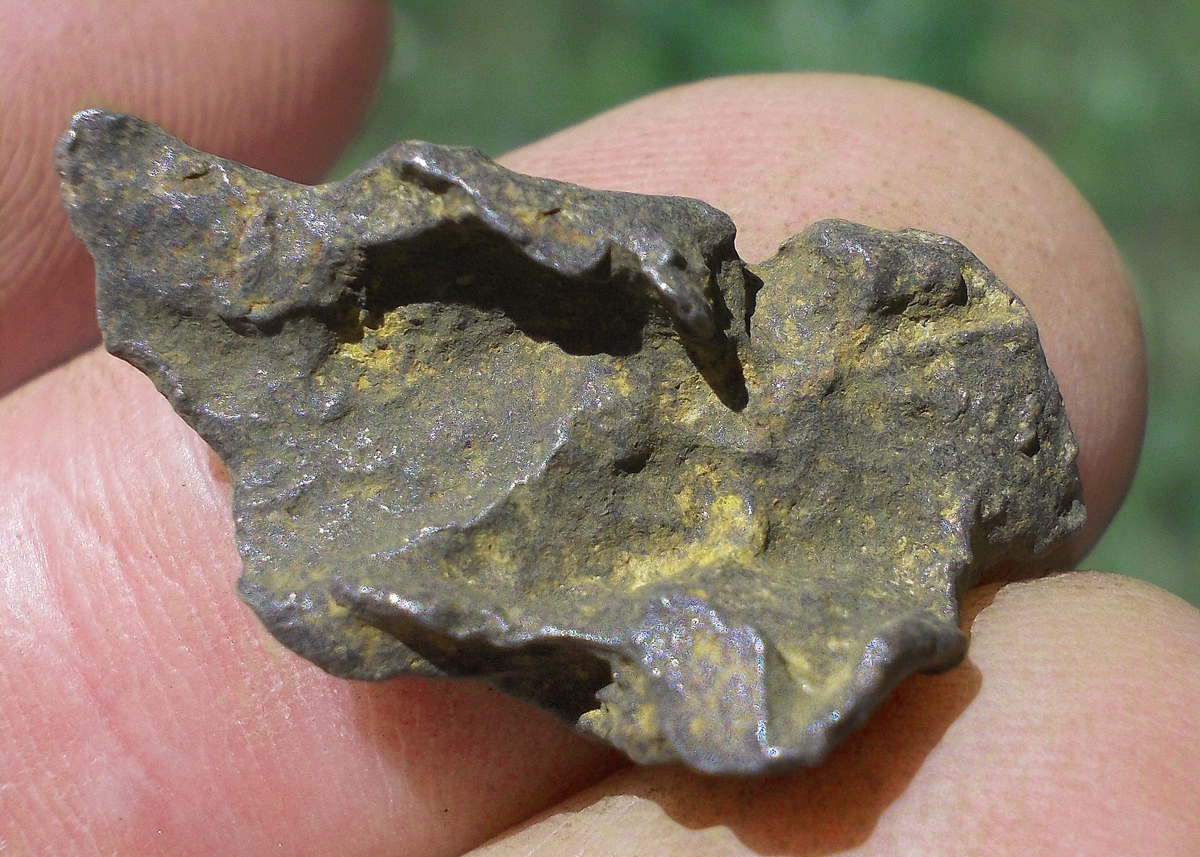
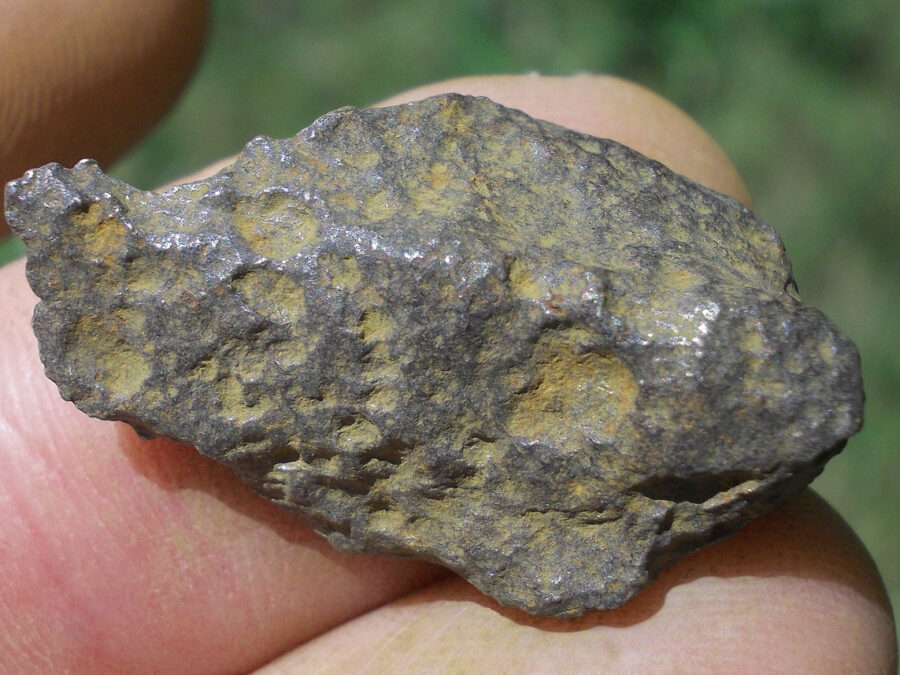
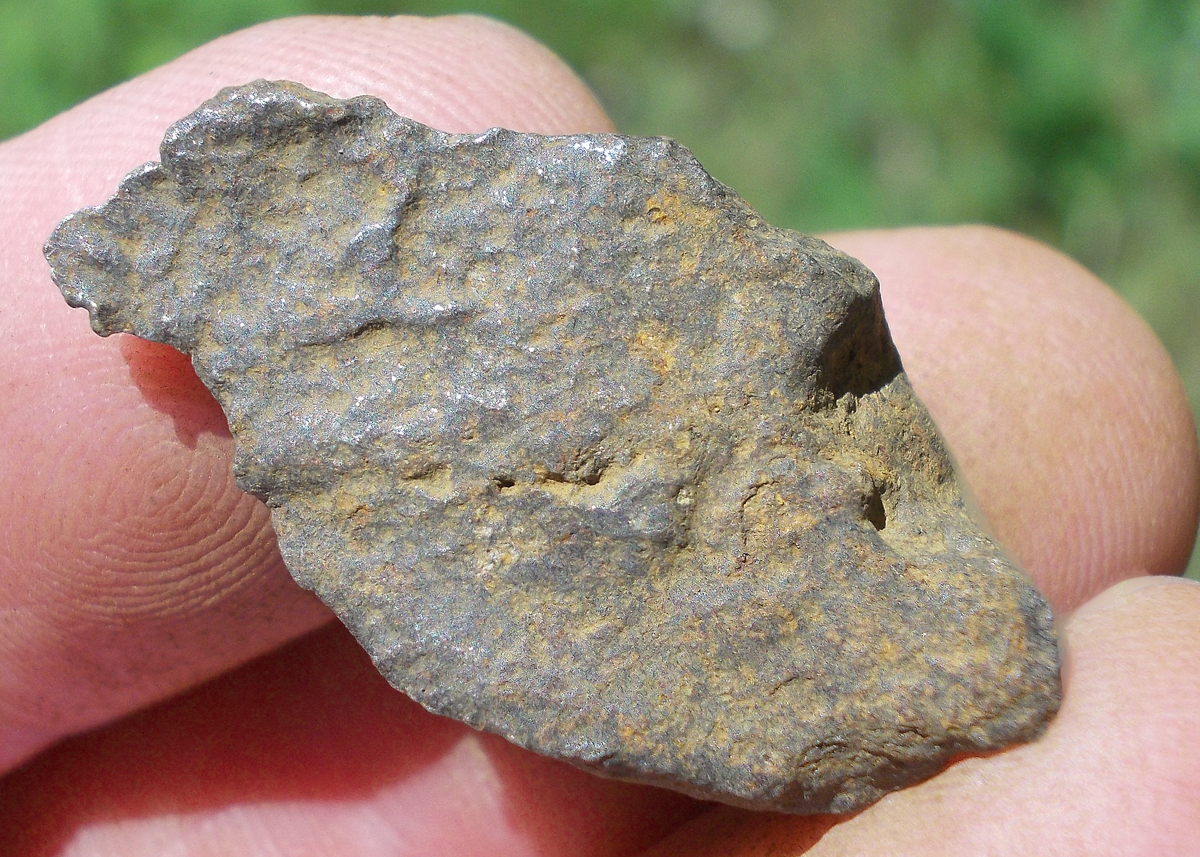
Turpan 003 est une météorite ferreuse.
Elle a été découverte en 2022 en Chine dans la province du Xinjiang.
Ce qui fait la particularité unique au Monde de cette météorite c’est sa structure naturelle pour une météorite ferreuse.
En effet, la structure des météorites métalliques est habituellement révélée par de l’acide.
Autre particularité unique, les inclusions silicatées vertes et avec bulles qu’elle possède.
Des études complémentaires sont en cours actuellement.
50,00€
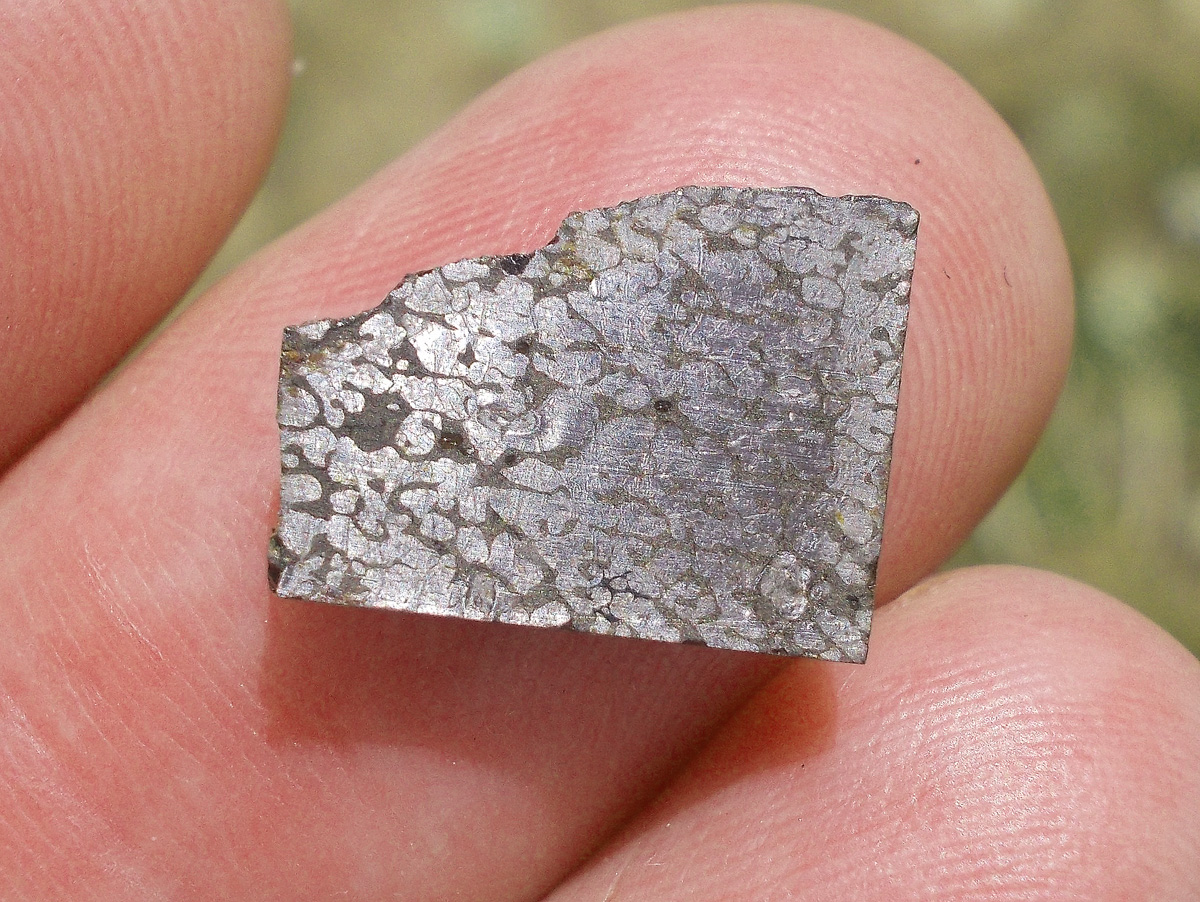
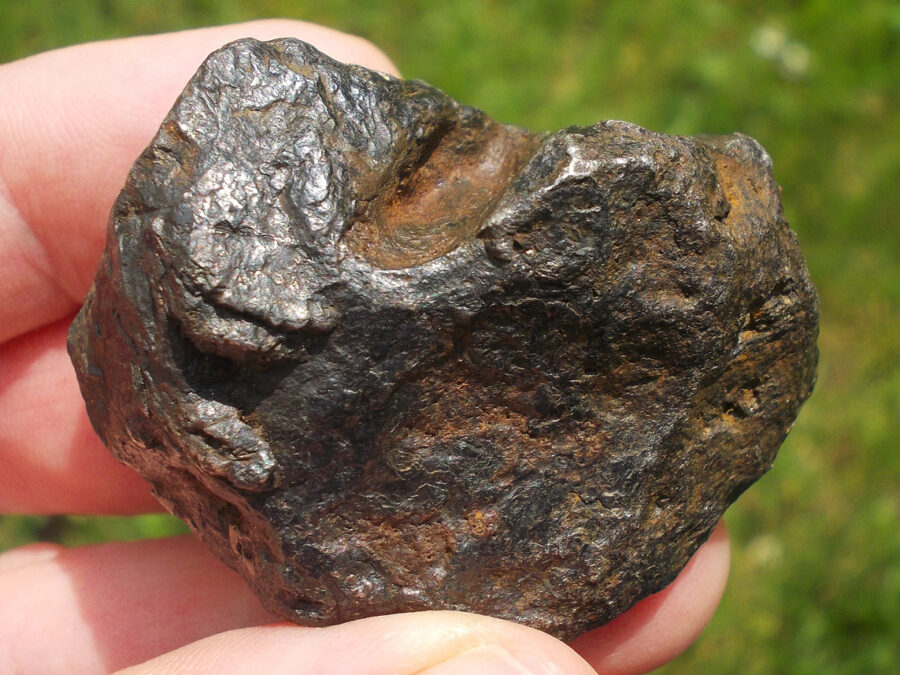
Turpan 003 est une météorite ferreuse.
Elle a été découverte en 2022 en Chine dans la province du Xinjiang.
Ce qui fait la particularité unique au Monde de cette météorite c’est sa structure naturelle pour une météorite ferreuse.
En effet, la structure des météorites métalliques est habituellement révélée par de l’acide.
Autre particularité unique, les inclusions silicatées vertes et avec bulles qu’elle possède.
Des études complémentaires sont en cours actuellement.
54,00€
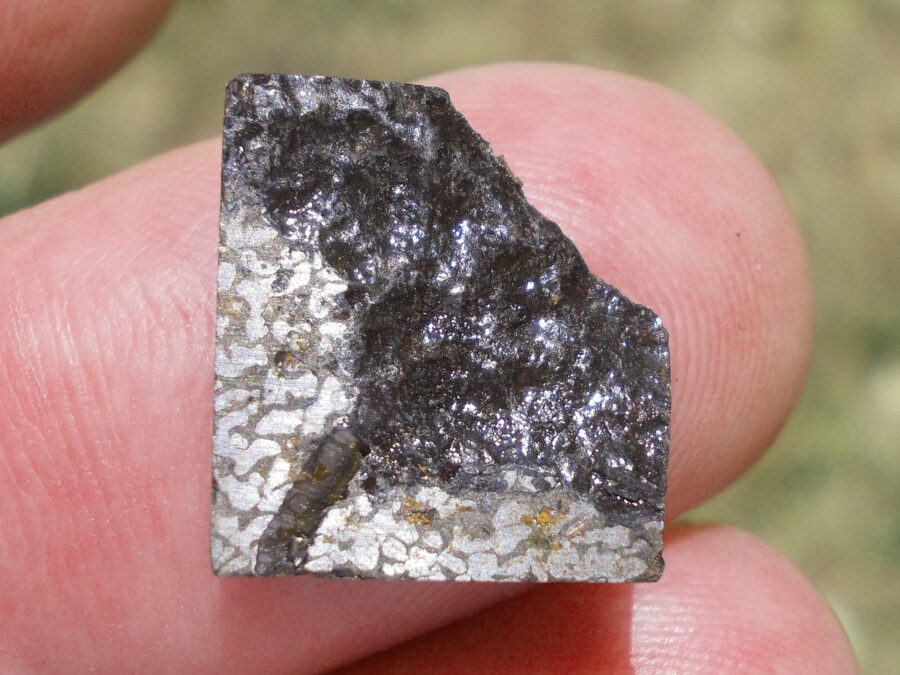
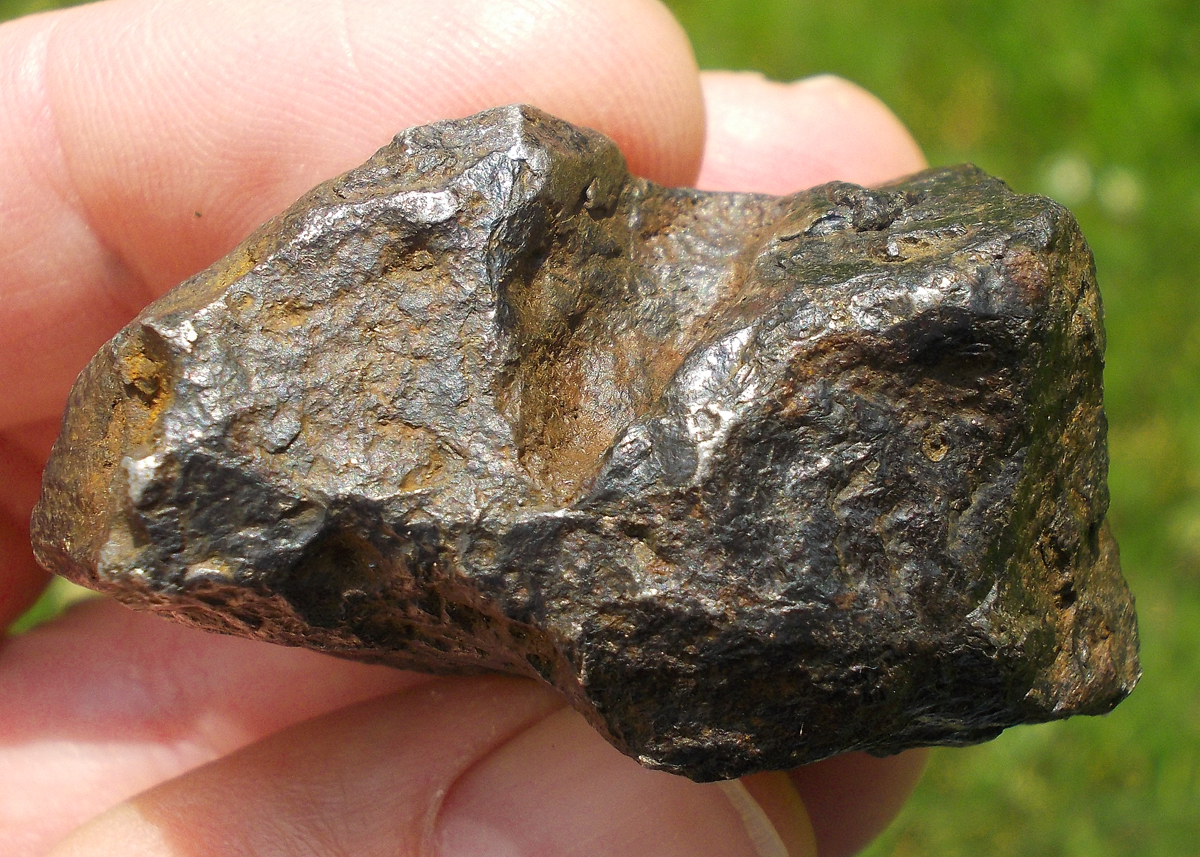
Turpan 003 est une météorite ferreuse.
Elle a été découverte en 2022 en Chine dans la province du Xinjiang.
Ce qui fait la particularité unique au Monde de cette météorite c’est sa structure naturelle pour une météorite ferreuse.
En effet, la structure des météorites métalliques est habituellement révélée par de l’acide.
Autre particularité unique, les inclusions silicatées vertes et avec bulles qu’elle possède.
Des études complémentaires sont en cours actuellement.
48,00€
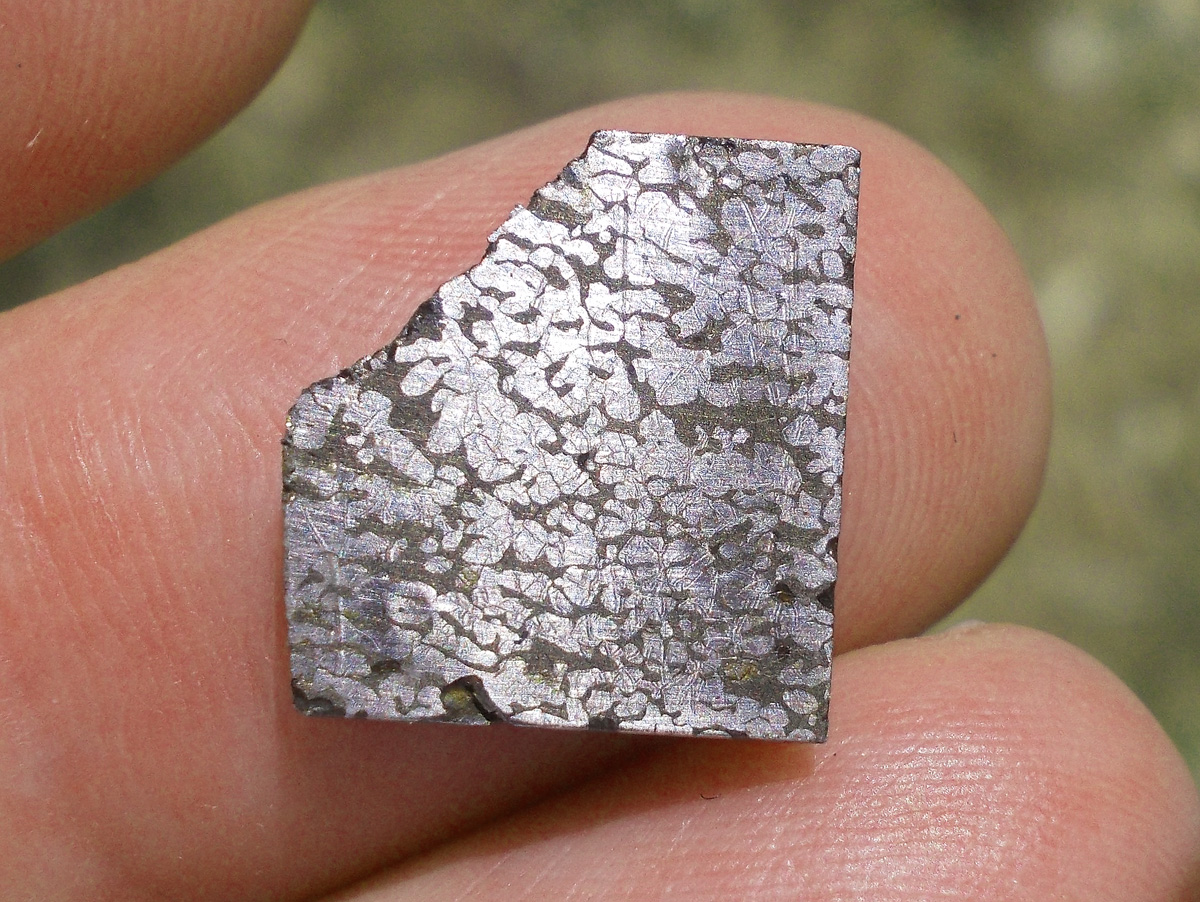
Turpan 003 est une météorite ferreuse.
Elle a été découverte en 2022 en Chine dans la province du Xinjiang.
Ce qui fait la particularité unique au Monde de cette météorite c’est sa structure naturelle pour une météorite ferreuse.
En effet, la structure des météorites métalliques est habituellement révélée par de l’acide.
Autre particularité unique, les inclusions silicatées vertes et avec bulles qu’elle possède.
Des études complémentaires sont en cours actuellement.
245,00€
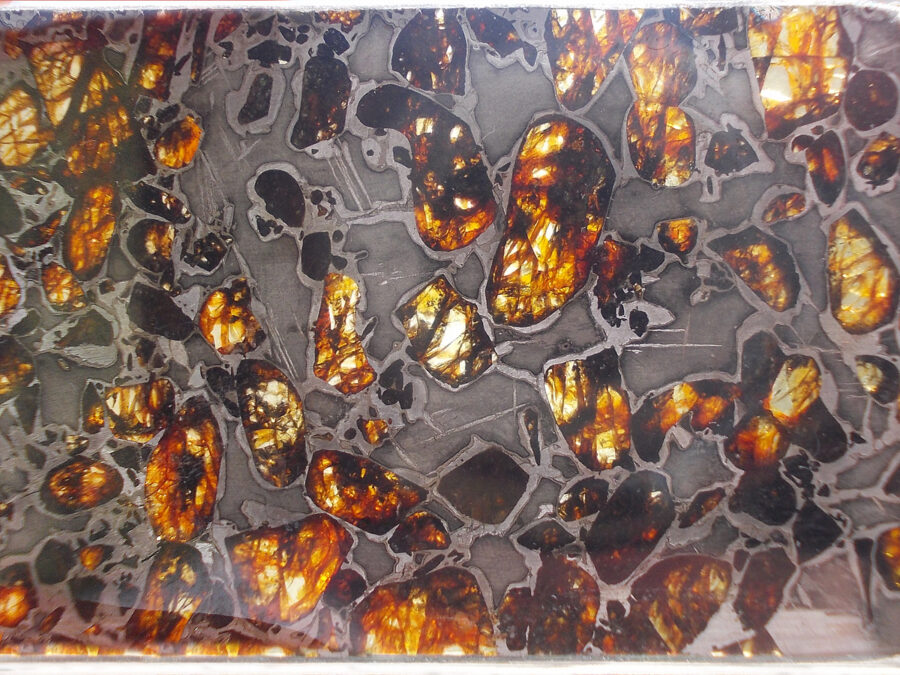
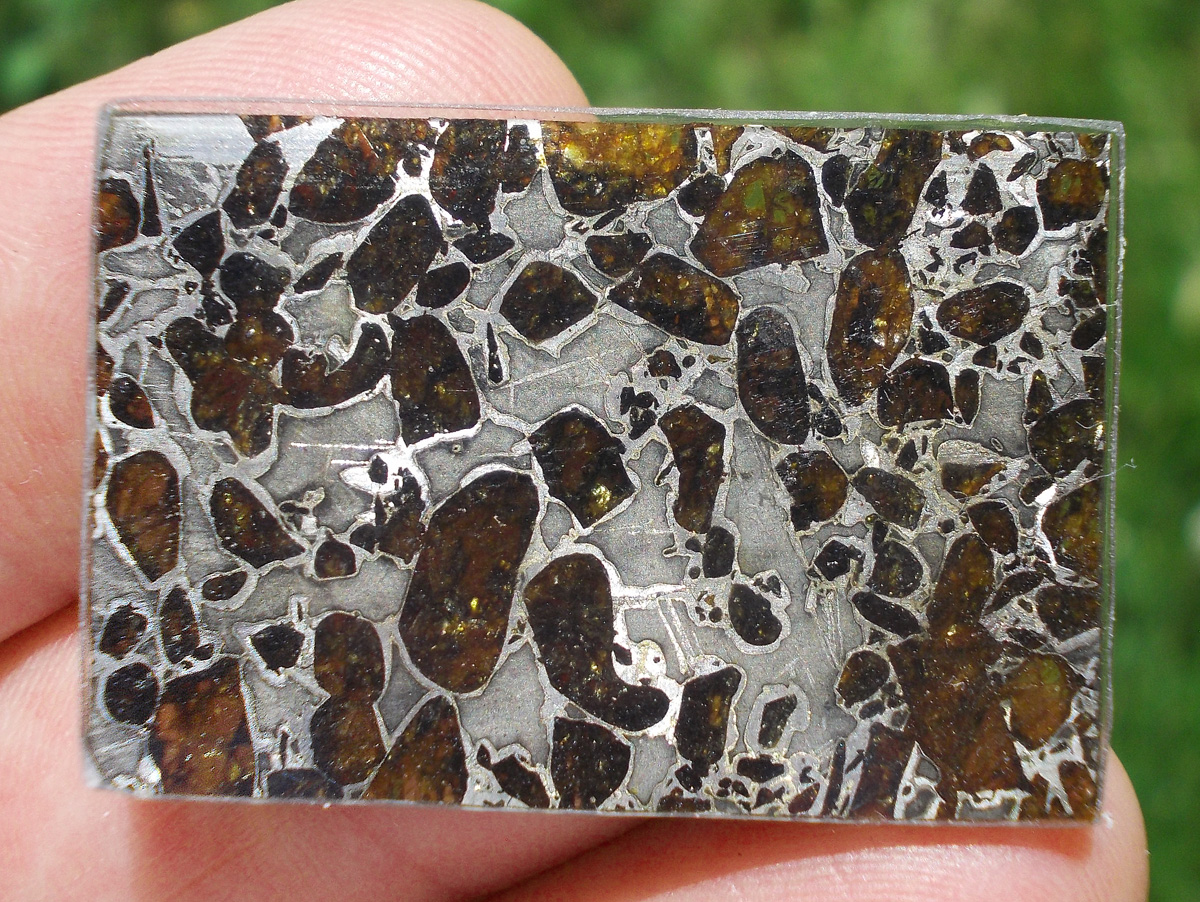
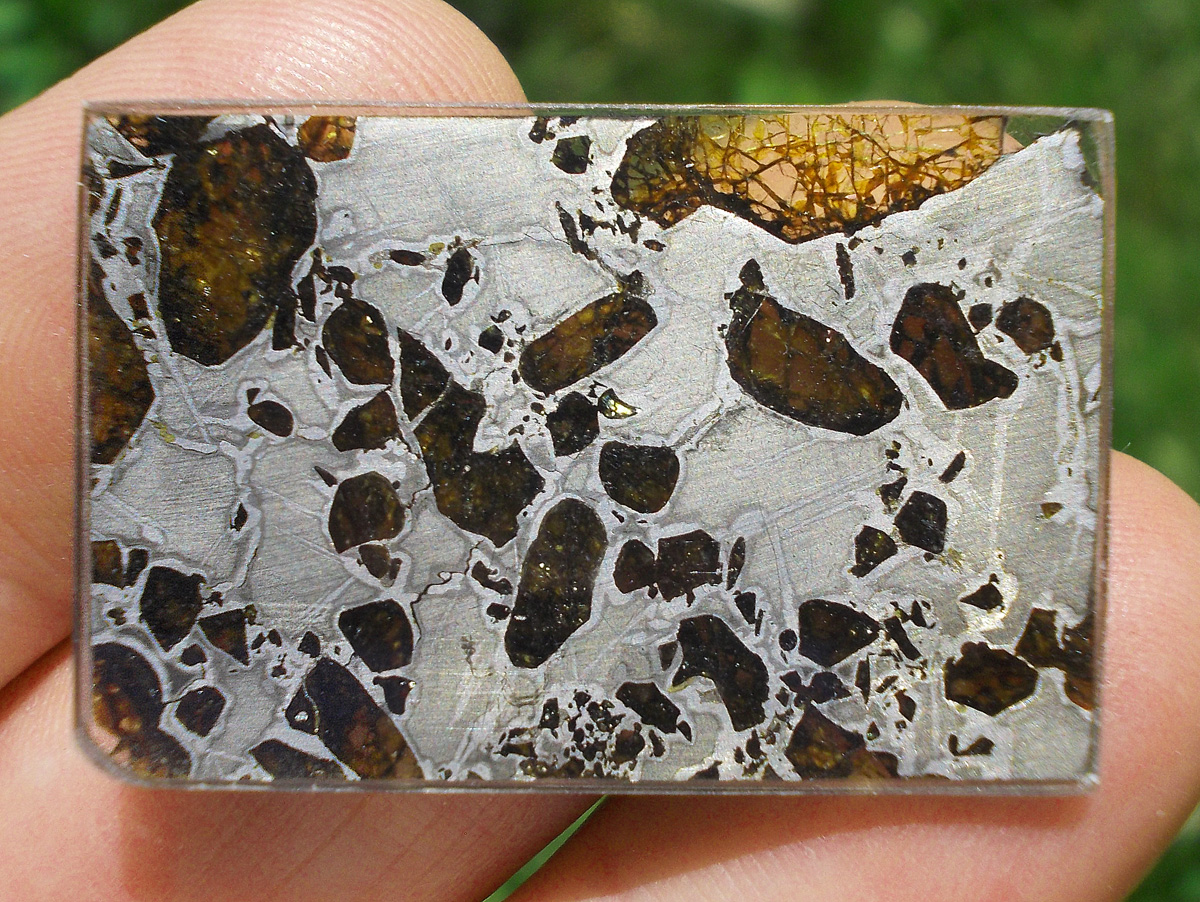
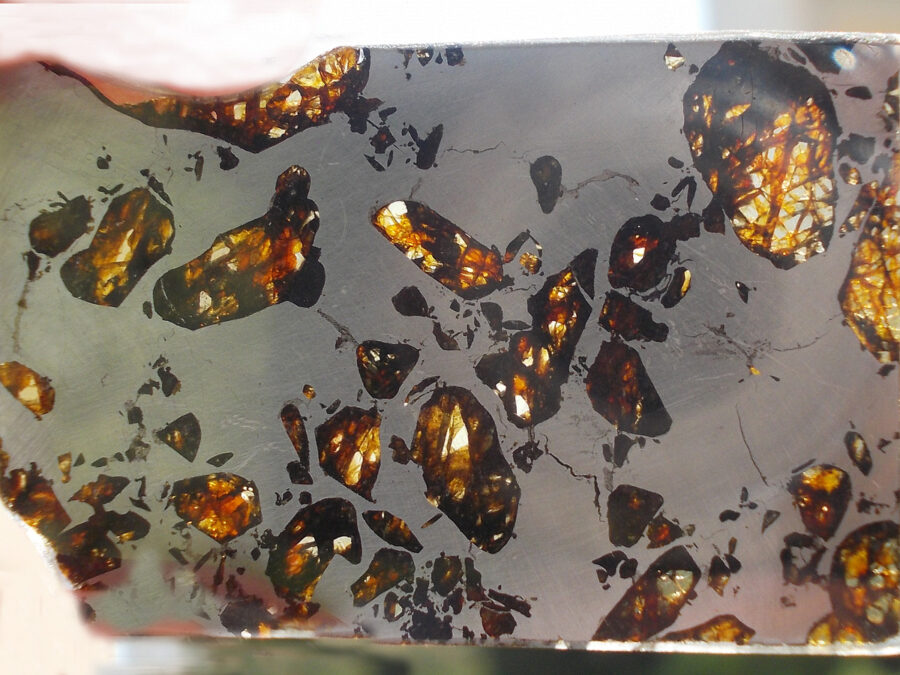
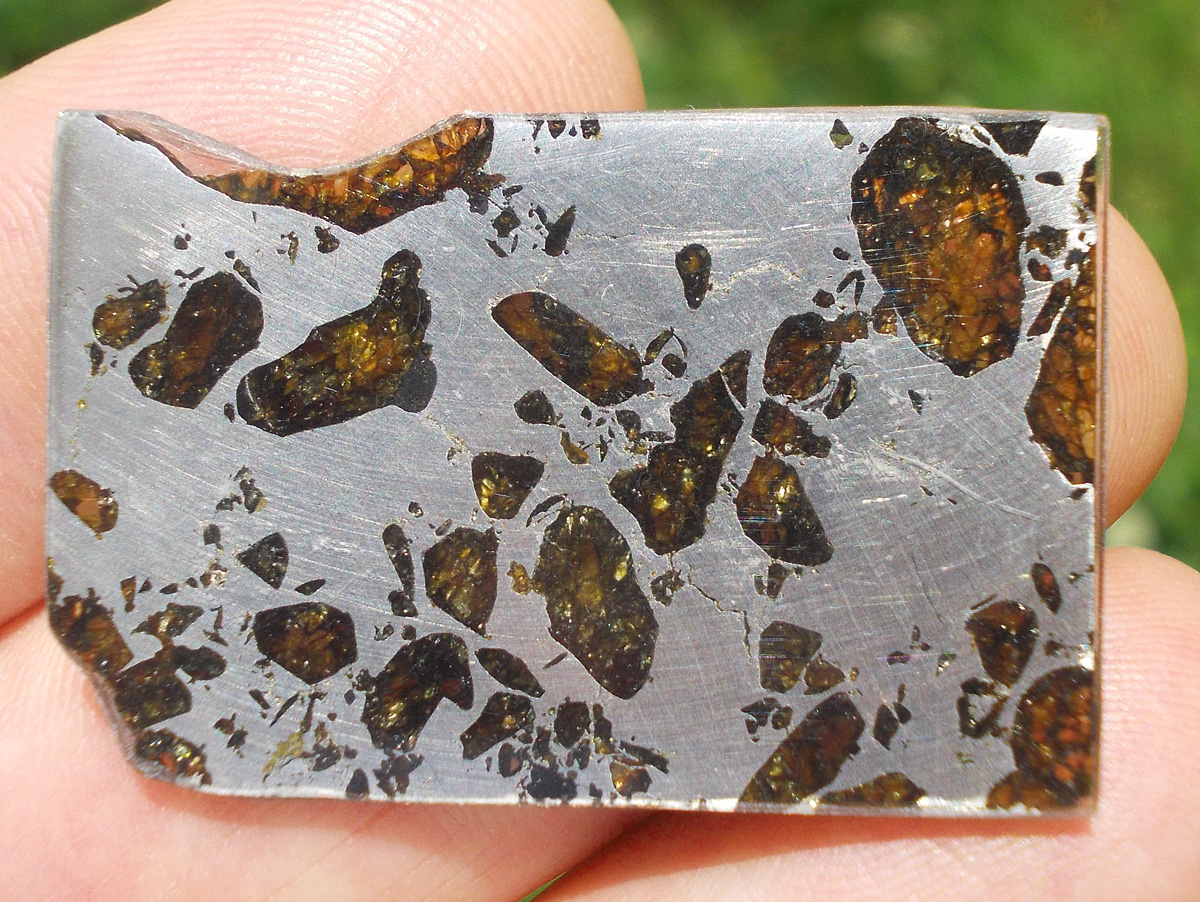
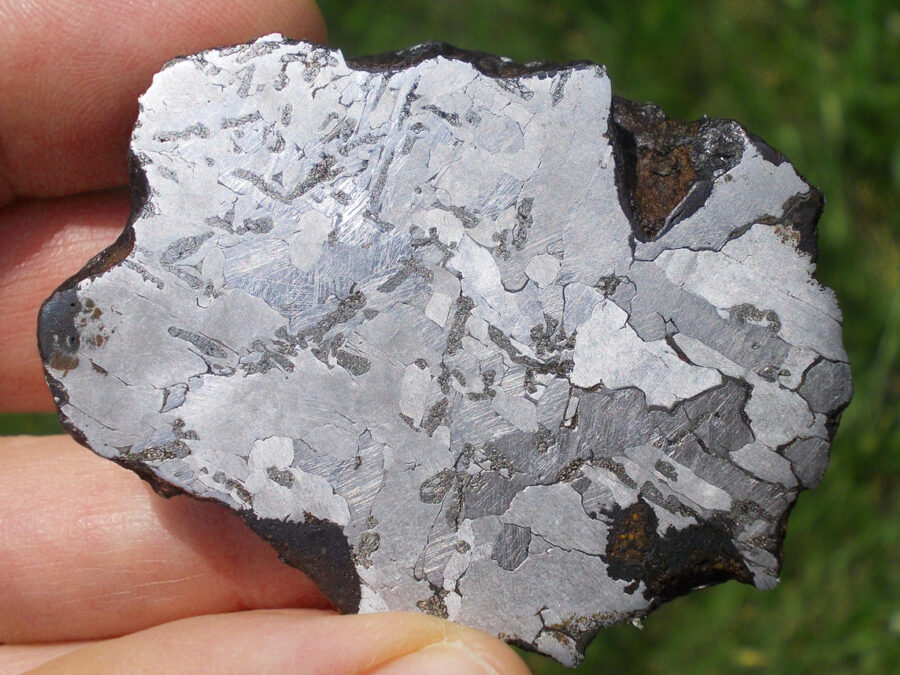
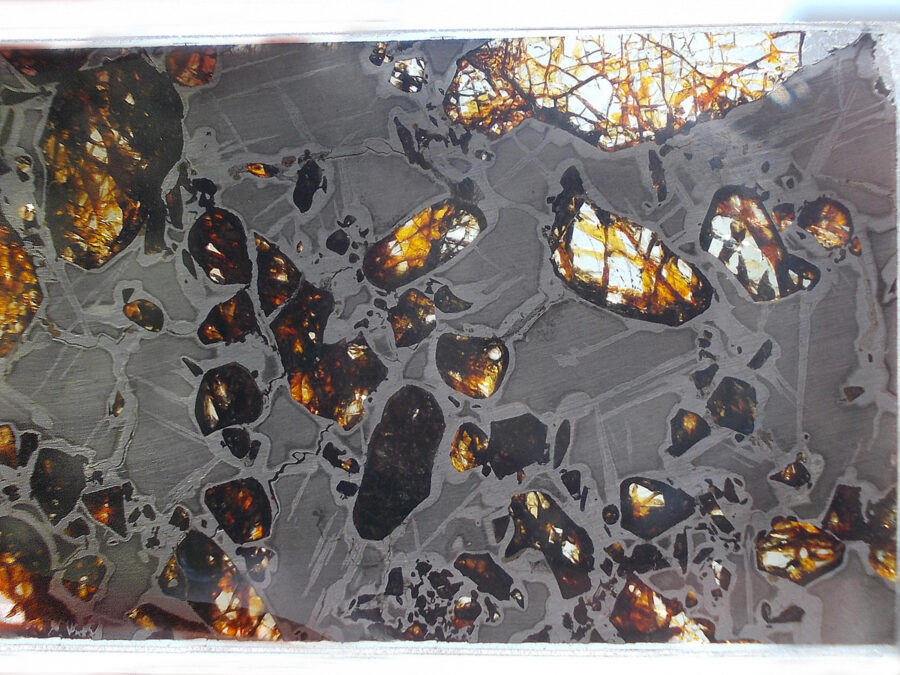
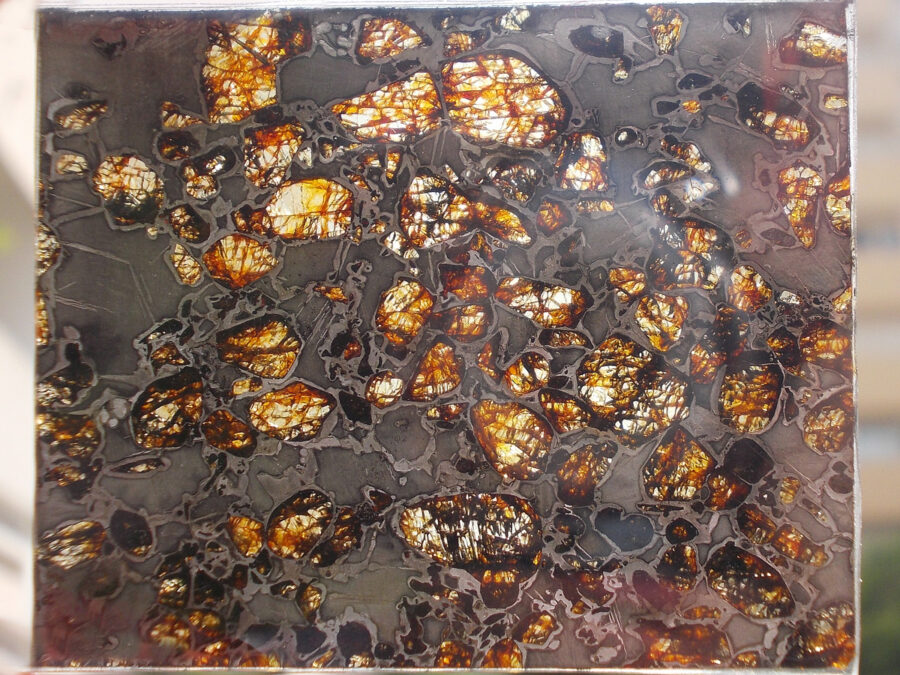
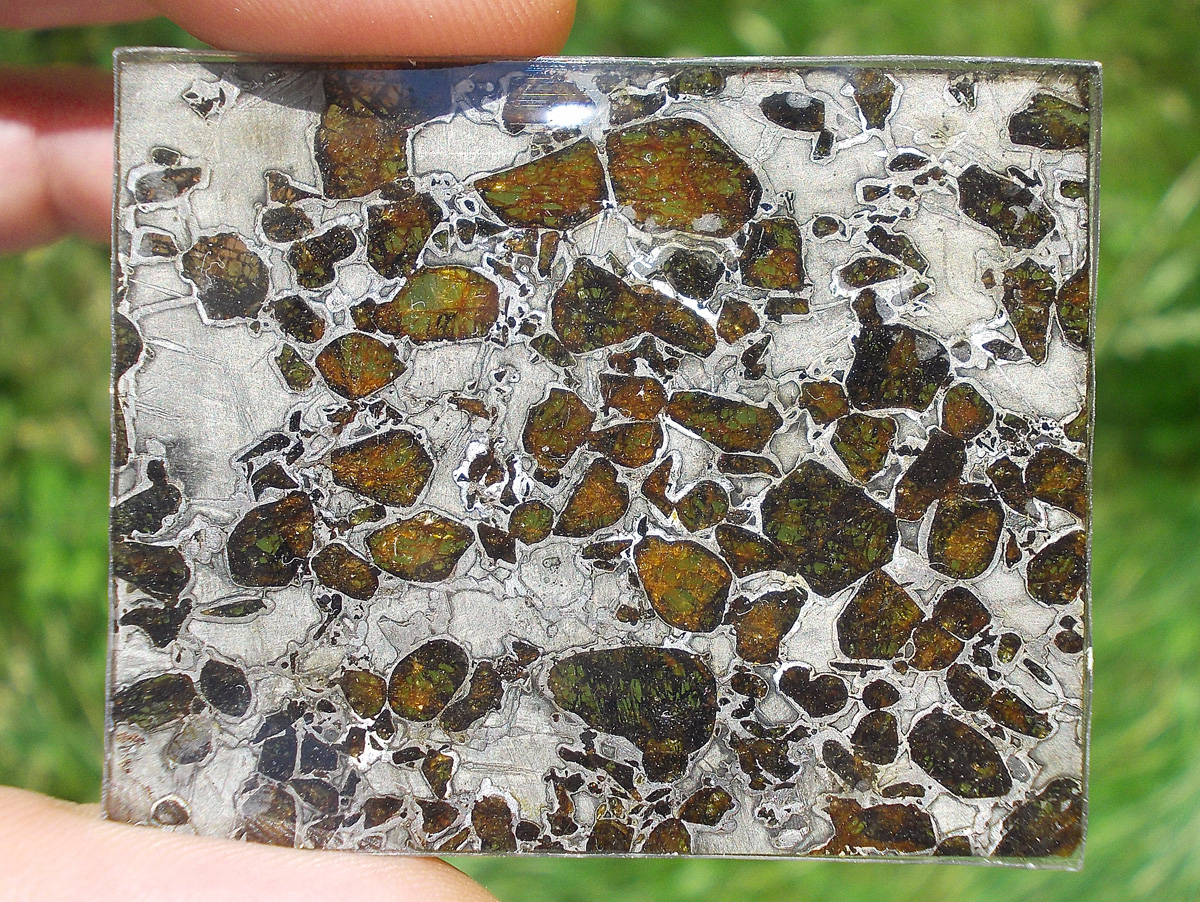
Gyarub Zangbo est une météorite de type pallasite découverte au Tibet en 2020 de seulement 18 kg.
La chimie minérale, les isotopes O et Cr de l’olivine et la phase métallique font de cette pallasite une pallasite carbonée anormale.
Gyarub Zangbo semble être une pallasite unique prélevée sur un astéroïde jusqu’ici non représenté dans la collection de pallasites.
Les pallasites sont des météorites pierre-fer uniques en leur genre, composées principalement d’olivine et de métal ferreux.
On pense qu’elles se sont formées dans la région limite entre le noyau et le manteau des astéroïdes, à l’intérieur des astéroïdes.
Les pallasites sont des météorites composées de cristaux d’olivine inclus dans une matrice de fer-nickel.
Les pallasites font partie des météorites les plus esthétiques.
Qualité exceptionnelle !
Tranche fine et translucide protégée par une très fine couche de résine.
Livrée avec certificat.
220,00€
Gyarub Zangbo est une météorite de type pallasite découverte au Tibet en 2020 de seulement 18 kg.
La chimie minérale, les isotopes O et Cr de l’olivine et la phase métallique font de cette pallasite une pallasite carbonée anormale.
Gyarub Zangbo semble être une pallasite unique prélevée sur un astéroïde jusqu’ici non représenté dans la collection de pallasites.
Les pallasites sont des météorites pierre-fer uniques en leur genre, composées principalement d’olivine et de métal ferreux.
On pense qu’elles se sont formées dans la région limite entre le noyau et le manteau des astéroïdes, à l’intérieur des astéroïdes.
Les pallasites sont des météorites composées de cristaux d’olivine inclus dans une matrice de fer-nickel.
Les pallasites font partie des météorites les plus esthétiques.
Qualité exceptionnelle !
Tranche fine et translucide protégée par une très fine couche de résine.
Livrée avec certificat.
200,00€
Gyarub Zangbo est une météorite de type pallasite découverte au Tibet en 2020 de seulement 18 kg.
La chimie minérale, les isotopes O et Cr de l’olivine et la phase métallique font de cette pallasite une pallasite carbonée anormale.
Gyarub Zangbo semble être une pallasite unique prélevée sur un astéroïde jusqu’ici non représenté dans la collection de pallasites.
Les pallasites sont des météorites pierre-fer uniques en leur genre, composées principalement d’olivine et de métal ferreux.
On pense qu’elles se sont formées dans la région limite entre le noyau et le manteau des astéroïdes, à l’intérieur des astéroïdes.
Les pallasites sont des météorites composées de cristaux d’olivine inclus dans une matrice de fer-nickel.
Les pallasites font partie des météorites les plus esthétiques.
Qualité exceptionnelle !
Tranche fine et translucide protégée par une très fine couche de résine.
Livrée avec certificat.
370,00€
Gyarub Zangbo est une météorite de type pallasite découverte au Tibet en 2020 de seulement 18 kg.
La chimie minérale, les isotopes O et Cr de l’olivine et la phase métallique font de cette pallasite une pallasite carbonée anormale.
Gyarub Zangbo semble être une pallasite unique prélevée sur un astéroïde jusqu’ici non représenté dans la collection de pallasites.
Les pallasites sont des météorites pierre-fer uniques en leur genre, composées principalement d’olivine et de métal ferreux.
On pense qu’elles se sont formées dans la région limite entre le noyau et le manteau des astéroïdes, à l’intérieur des astéroïdes.
Les pallasites sont des météorites composées de cristaux d’olivine inclus dans une matrice de fer-nickel.
Les pallasites font partie des météorites les plus esthétiques.
Qualité exceptionnelle !
Tranche fine et translucide protégée par une très fine couche de résine.
Livrée avec certificat.
66,00€
Turpan 003 est une météorite ferreuse.
Elle a été découverte en 2022 en Chine dans la province du Xinjiang.
Ce qui fait la particularité unique au Monde de cette météorite c’est sa structure naturelle pour une météorite ferreuse.
En effet, la structure des météorites métalliques est habituellement révélée par de l’acide.
Autre particularité unique, les inclusions silicatées vertes et avec bulles qu’elle possède.
Des études complémentaires sont en cours actuellement.
70,00€
Turpan 003 est une météorite ferreuse.
Elle a été découverte en 2022 en Chine dans la province du Xinjiang.
Ce qui fait la particularité unique au Monde de cette météorite c’est sa structure naturelle pour une météorite ferreuse.
En effet, la structure des météorites métalliques est habituellement révélée par de l’acide.
Autre particularité unique, les inclusions silicatées vertes et avec bulles qu’elle possède.
Des études complémentaires sont en cours actuellement.
38,00€
Turpan 003 est une météorite ferreuse.
Elle a été découverte en 2022 en Chine dans la province du Xinjiang.
Ce qui fait la particularité unique au Monde de cette météorite c’est sa structure naturelle pour une météorite ferreuse.
En effet, la structure des météorites métalliques est habituellement révélée par de l’acide.
Autre particularité unique, les inclusions silicatées vertes et avec bulles qu’elle possède.
Des études complémentaires sont en cours actuellement.
72,00€
Turpan 003 est une météorite ferreuse.
Elle a été découverte en 2022 en Chine dans la province du Xinjiang.
Ce qui fait la particularité unique au Monde de cette météorite c’est sa structure naturelle pour une météorite ferreuse.
En effet, la structure des météorites métalliques est habituellement révélée par de l’acide.
Autre particularité unique, les inclusions silicatées vertes et avec bulles qu’elle possède.
Des études complémentaires sont en cours actuellement.
580,00€
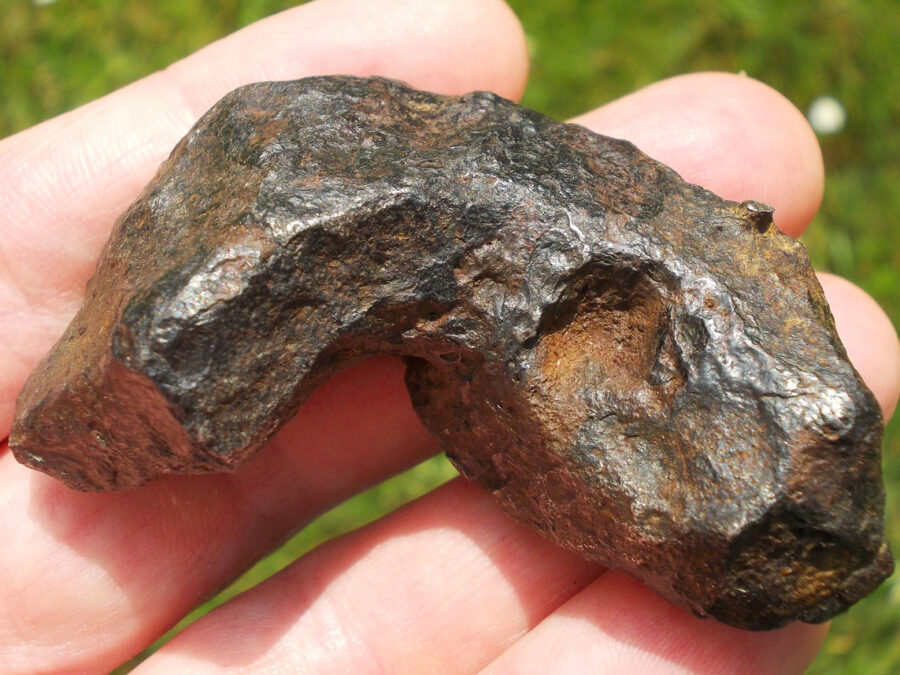
Morasko est une météorite ferreuse de type IAB-MG.
Elle a été découverte pour la première fois en Pologne en 1914.
Top qualité !
515,00€
Morasko est une météorite ferreuse de type IAB-MG.
Elle a été découverte pour la première fois en Pologne en 1914.
Top qualité !
531,00€
Morasko est une météorite ferreuse de type IAB-MG.
Elle a été découverte pour la première fois en Pologne en 1914.
Top qualité !
14,00€
La météorite de Sikhote-Alin est une météorite ferreuse tombée en 1947 en Sibérie. Cette chute est unique dans l’histoire des météorites, au vu des 70 tonnes qui ont survécu à la traversée de l’atmosphère terrestre.
Une chute de plus en plus difficile à trouver.
34,00€
La météorite de Sikhote-Alin est une météorite ferreuse tombée en 1947 en Sibérie. Cette chute est unique dans l’histoire des météorites, au vu des 70 tonnes qui ont survécu à la traversée de l’atmosphère terrestre.
Une chute de plus en plus difficile à trouver.